


|
||
|
||
Banking Trojans have been around for decades and still persist to this day because they effectively siphon off victims’ financial data and savings. And one of the latest additions to the ever-growing malware type—ToxicPanda—has been plaguing bank customers throughout Asia and Latin America since October 2024.
ToxicPanda primarily affects Android devices. Its main goal is to initiate money transfers from compromised devices via account takeovers (ATOs) using a technique called “on-device fraud (ODF).” It bypasses bank countermeasures to enforce user identity verification and authentication as well as behavioral detection techniques to identify suspicious money transfers.
Cleafy analyzed the malware in great depth and identified 26 indicators of compromise (IoCs), including 21 domain names in their report. The WhoisXML API research team expanded the list of 21 domain IoCs through a DNS deep dive and uncovered more connected artifacts, including:
A sample of the additional artifacts obtained from our analysis is available for download from our website.
As per usual, we began our study by looking for more information about the IoCs.
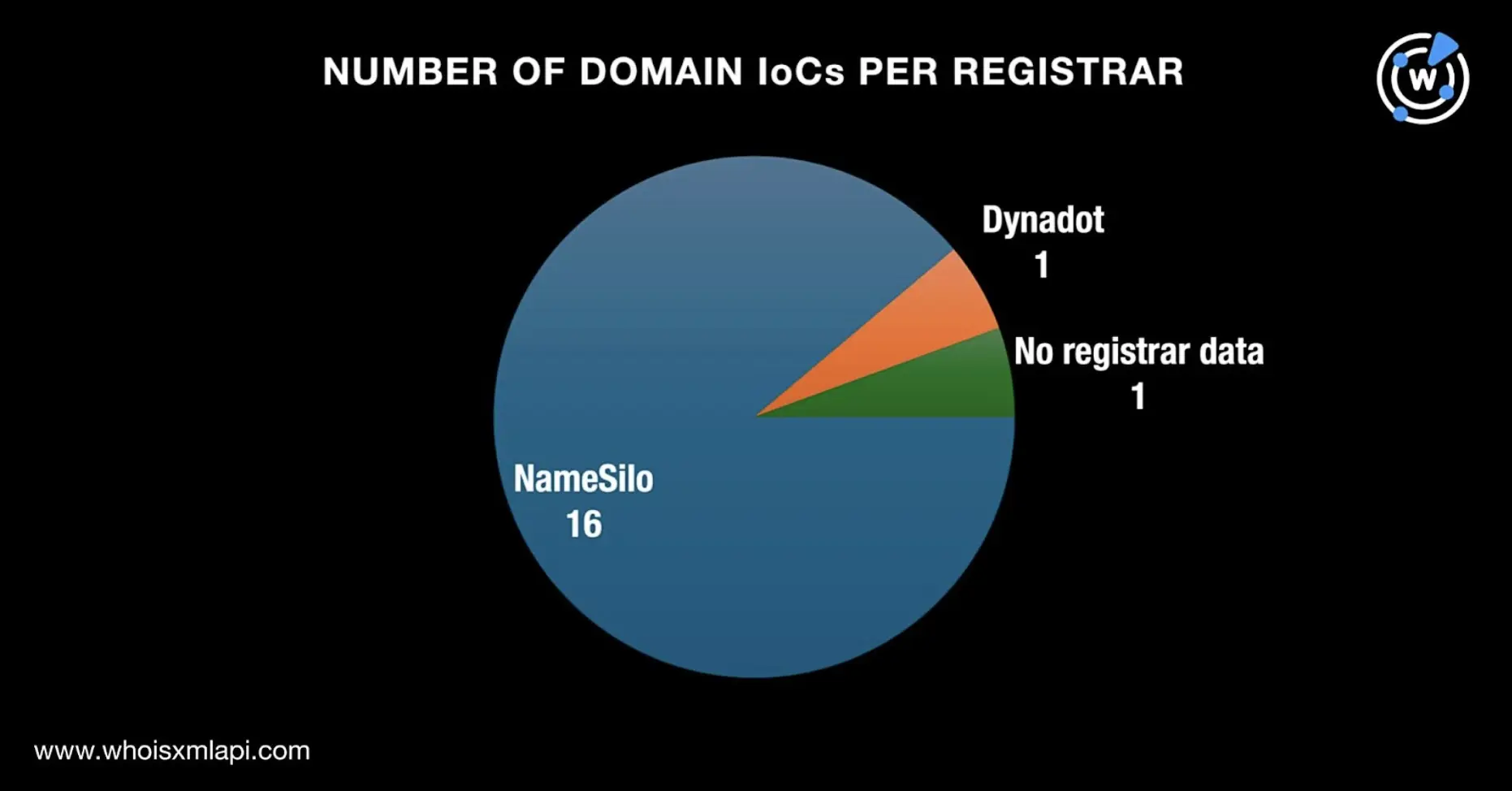
We queried the 21 domains tagged as IoCs on Bulk WHOIS Lookup, which revealed that only 18 of them had current WHOIS records. The lookup results showed that:
We also queried the 21 domains tagged as IoCs on DNS Chronicle API and found that they resolved to 122 IP addresses between 8 July 2020 and 27 November 2024. Take a look at five examples below.
| DOMAIN IoC | START DATE | END DATE | NUMBER OF IP RESOLUTIONS |
|---|---|---|---|
| cpt[.]lol | 7 July 2023 | 7 August 2024 | 4 |
| dksu[.]top | 16 August 2024 | 12 September 2024 | 14 |
| freebasic[.]cn | 16 August 2020 | 27 November 2024 | 71 |
| mixcom[.]one | 21 September 2024 | 10 November 2024 | 8 |
| unk[.]lol | 14 April 2023 | 27 April 2024 | 3 |
We kicked off our expansion analysis by querying the 21 domains tagged as IoCs on WHOIS History API, which gave us seven email addresses from their historical WHOIS records. Further scrutiny of the email addresses showed that five of them were public.
Querying the five public email addresses on Reverse WHOIS API provided us with six email-connected domains after duplicates and the IoCs were filtered out.
Next up, we queried the 21 domains tagged as IoCs on DNS Lookup API and found that they resolved to seven unique IP addresses.
Threat Intelligence API revealed that four of the seven IP addresses were malicious. The IP address 172[.]67[.]176[.]238, for instance, was associated with phishing, malware distribution, attacks, and generic threats. The IP address 104[.]21[.]6[.]160, meanwhile, has figured in malware distribution, phishing, and generic threats.
This post only contains a snapshot of the full research. Download the complete findings and a sample of the additional artifacts on our website or contact us to discuss your intelligence needs for threat detection and response or other cybersecurity use cases.
Disclaimer: We take a cautionary stance toward threat detection and aim to provide relevant information to help protect against potential dangers. Consequently, it is possible that some entities identified as “threats” or “malicious” may eventually be deemed harmless upon further investigation or changes in context. We strongly recommend conducting supplementary investigations to corroborate the information provided herein.
Sponsored byRadix

Sponsored byCSC

Sponsored byVerisign

Sponsored byDNIB.com

Sponsored byIPv4.Global

Sponsored byVerisign

Sponsored byWhoisXML API
