

 In 2026, internet infrastructure will be reshaped by geopolitics, grid constraints, and regulatory shifts. Firms that treat data location, power access, and legal compliance as strategic priorities will gain competitive advantage.
In 2026, internet infrastructure will be reshaped by geopolitics, grid constraints, and regulatory shifts. Firms that treat data location, power access, and legal compliance as strategic priorities will gain competitive advantage.
 As telecom networks grow more interconnected, local outages can now trigger regional or national disruptions. A recent article by Ookla outlines five critical steps operators must follow to prevent small faults from cascading into systemic failures.
As telecom networks grow more interconnected, local outages can now trigger regional or national disruptions. A recent article by Ookla outlines five critical steps operators must follow to prevent small faults from cascading into systemic failures.
 While Starlink dominates the low-Earth orbit internet race, rivals like OneWeb, Telesat, Amazon's Project Kuiper, and Europe's IRIS² are slowly building capacity, buoyed by geopolitical necessity, state support, and commercial partnerships.
While Starlink dominates the low-Earth orbit internet race, rivals like OneWeb, Telesat, Amazon's Project Kuiper, and Europe's IRIS² are slowly building capacity, buoyed by geopolitical necessity, state support, and commercial partnerships.
 Over two years of war, Israel has decimated Gaza's ICT infrastructure, crippling connectivity, impeding emergency response, and isolating civilians from the digital world, while cementing long-standing control over telecommunications under the guise of national security.
Over two years of war, Israel has decimated Gaza's ICT infrastructure, crippling connectivity, impeding emergency response, and isolating civilians from the digital world, while cementing long-standing control over telecommunications under the guise of national security.
 Big Tech firms should back Africa's AI future by investing in its vast energy resources and infrastructure needs. Doing so offers a strategic answer to growing data demands and an opportunity for shared prosperity.
Big Tech firms should back Africa's AI future by investing in its vast energy resources and infrastructure needs. Doing so offers a strategic answer to growing data demands and an opportunity for shared prosperity.
 Broadband infrastructure is advancing rapidly, from multi-gigabit cable and fiber networks to next-generation fixed wireless and satellite systems. With speeds reaching up to 25 Gbps for consumers and 1 Tbps in orbit, these developments mark a pivotal shift in connectivity, setting the stage for more scalable, flexible, and high-capacity networks.
Broadband infrastructure is advancing rapidly, from multi-gigabit cable and fiber networks to next-generation fixed wireless and satellite systems. With speeds reaching up to 25 Gbps for consumers and 1 Tbps in orbit, these developments mark a pivotal shift in connectivity, setting the stage for more scalable, flexible, and high-capacity networks.
 Earlier this week, Poland’s new President, Karol Nawrocki, vetoed amendments to the Act on Assistance to Citizens of Ukraine, provoking debate over critical satellite connectivity. Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Digital Affairs Krzysztof Gawkowski warned that the veto “de facto switched off Starlink for Ukraine,” potentially disrupting connectivity for hospitals, schools, and government operations.
Earlier this week, Poland’s new President, Karol Nawrocki, vetoed amendments to the Act on Assistance to Citizens of Ukraine, provoking debate over critical satellite connectivity. Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Digital Affairs Krzysztof Gawkowski warned that the veto “de facto switched off Starlink for Ukraine,” potentially disrupting connectivity for hospitals, schools, and government operations.
 There was a recent article in the Wall Street Journal that noted that the business world still uses a lot of landline telephones. Landline telephones have been steadily disappearing from homes, but are still not gone. I see ISPs still selling a telephone line to 10% or more of passings, and surveys show that the average residential landline penetration rate is still somewhere between 15% and 20%.
There was a recent article in the Wall Street Journal that noted that the business world still uses a lot of landline telephones. Landline telephones have been steadily disappearing from homes, but are still not gone. I see ISPs still selling a telephone line to 10% or more of passings, and surveys show that the average residential landline penetration rate is still somewhere between 15% and 20%.
 On 17 May 1865, 20 European states convened to establish the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) to streamline the clunky process of sending telegraph messages across borders. 160 years later, ITU's anniversary is more than a mere commemorative moment; it is a stark reminder that multilateral cooperation is beneficial and necessary in our increasingly interconnected world.
On 17 May 1865, 20 European states convened to establish the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) to streamline the clunky process of sending telegraph messages across borders. 160 years later, ITU's anniversary is more than a mere commemorative moment; it is a stark reminder that multilateral cooperation is beneficial and necessary in our increasingly interconnected world.
 This past week offered a striking illustration of the pace and scale at which our shared orbital environment is evolving. In less than 24 hours, six rockets were launched from different parts of the globe, each contributing to the rapid expansion of low Earth orbit (LEO) infrastructure. China deployed a new set of Guowang satellites, while SpaceX launched two batches of Starlink satellites - one from Vandenberg in California and another from Cape Canaveral in Florida. United Launch Alliance (ULA) successfully placed Amazon's Kuiper satellites into orbit...
This past week offered a striking illustration of the pace and scale at which our shared orbital environment is evolving. In less than 24 hours, six rockets were launched from different parts of the globe, each contributing to the rapid expansion of low Earth orbit (LEO) infrastructure. China deployed a new set of Guowang satellites, while SpaceX launched two batches of Starlink satellites - one from Vandenberg in California and another from Cape Canaveral in Florida. United Launch Alliance (ULA) successfully placed Amazon's Kuiper satellites into orbit...
 Today, the Supreme Court will consider a challenge to the universal service subsidy program established soon after the introduction of telephone service by the AT&T Bell System and later officially adopted by the FCC as mandated by a 1996 law.1, 2 Universal service funding supports access to telephone and broadband service by subscribers in rural locales that commercial ventures will not serve absent a subsidy.
Today, the Supreme Court will consider a challenge to the universal service subsidy program established soon after the introduction of telephone service by the AT&T Bell System and later officially adopted by the FCC as mandated by a 1996 law.1, 2 Universal service funding supports access to telephone and broadband service by subscribers in rural locales that commercial ventures will not serve absent a subsidy.
 NVIDIA recently issued its third annual State of AI in Telecommunications report. The company manufactures many of the cards used in AI data centers, so the company is clearly focused on AI adoption. NVIDIA issues similar reports for other industries. The 2025 report is the result of a survey that NVIDIA administered to 450 telecom professionals across the globe.
NVIDIA recently issued its third annual State of AI in Telecommunications report. The company manufactures many of the cards used in AI data centers, so the company is clearly focused on AI adoption. NVIDIA issues similar reports for other industries. The 2025 report is the result of a survey that NVIDIA administered to 450 telecom professionals across the globe.
 A new resource dedicated to small and medium-sized digital infrastructure providers highlights the benefits of incorporating sustainability into their operations, offers a consolidated list of best practices and recommendations, and shares additional resources to help make practical changes to save time, energy, and money.
A new resource dedicated to small and medium-sized digital infrastructure providers highlights the benefits of incorporating sustainability into their operations, offers a consolidated list of best practices and recommendations, and shares additional resources to help make practical changes to save time, energy, and money.
 The debate surrounding network usage fees in Brazil has intensified following the approval of Bill 469/2024 by the House of Representatives' Communications Committee in early December 2024. This bill prohibits telecommunications operators from charging internet companies based on data traffic. While this is merely a preliminary step in a lengthy legislative process, it signals that proposals from telecom companies to implement network usage fees are unlikely to gain traction.
The debate surrounding network usage fees in Brazil has intensified following the approval of Bill 469/2024 by the House of Representatives' Communications Committee in early December 2024. This bill prohibits telecommunications operators from charging internet companies based on data traffic. While this is merely a preliminary step in a lengthy legislative process, it signals that proposals from telecom companies to implement network usage fees are unlikely to gain traction.
 I recently saw that AT&T is offering a $10,000 reward to anybody who provides information that leads to the arrest and conviction of people stealing copper wiring. The particular announcement is related to a recent theft of copper in South Dallas, Texas, but there have been numerous other thefts. This is not a small problem, and the estimated value of stolen telephone copper is between $1.5 and $2 billion annually.
I recently saw that AT&T is offering a $10,000 reward to anybody who provides information that leads to the arrest and conviction of people stealing copper wiring. The particular announcement is related to a recent theft of copper in South Dallas, Texas, but there have been numerous other thefts. This is not a small problem, and the estimated value of stolen telephone copper is between $1.5 and $2 billion annually.
 US Senators Move to Shield Undersea Internet Cables from Global Threats
US Senators Move to Shield Undersea Internet Cables from Global Threats Verizon and AWS Expand Network Ties to Meet AI Data Demands
Verizon and AWS Expand Network Ties to Meet AI Data Demands Smuggled Phone Reveals North Korea’s Regime Captures User Screens Every Five Minutes, Censors Texting
Smuggled Phone Reveals North Korea’s Regime Captures User Screens Every Five Minutes, Censors Texting Chinese Hackers Exploit U.S. Telecom Systems, Eviction Efforts Lag
Chinese Hackers Exploit U.S. Telecom Systems, Eviction Efforts Lag Meta’s $10 Billion Plan to Build the World’s Largest Subsea Cable Network
Meta’s $10 Billion Plan to Build the World’s Largest Subsea Cable Network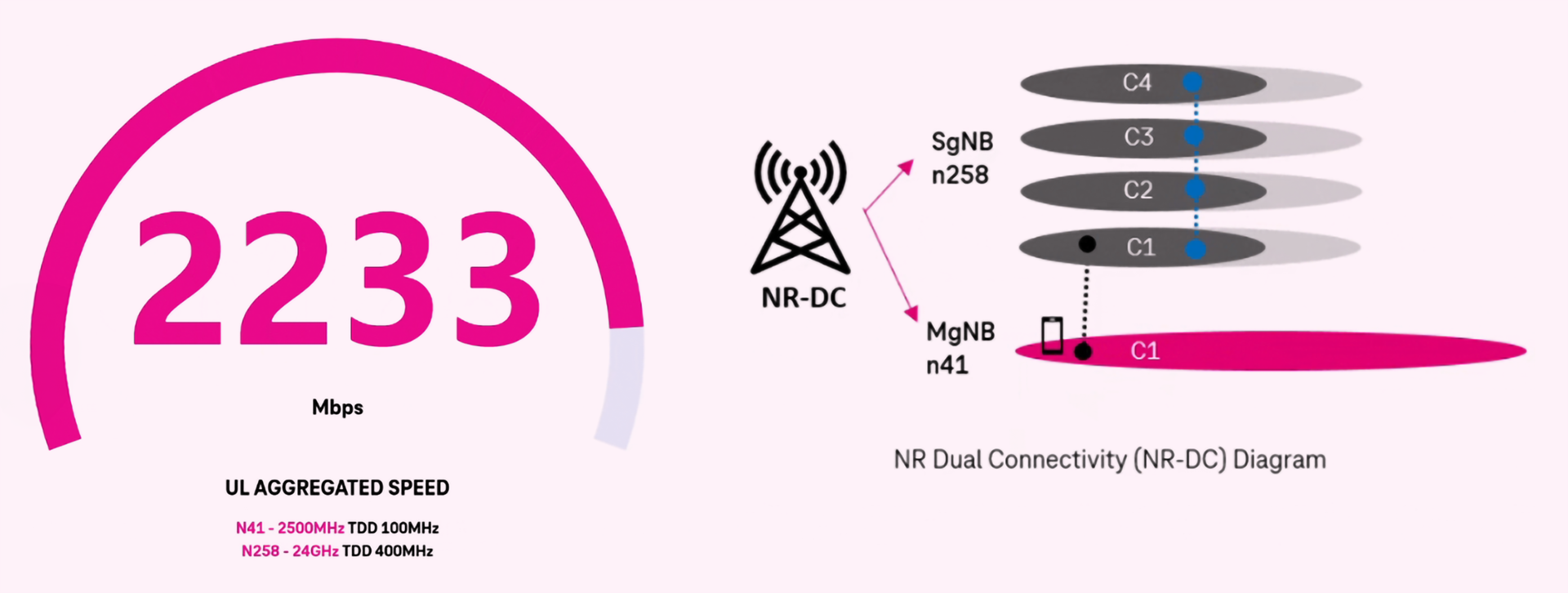 T-Mobile Breaks Upload Speed Record with New 5G Dual Connectivity
T-Mobile Breaks Upload Speed Record with New 5G Dual Connectivity EU Internet Advocates Push Back Against Telecom “Fair-Share” Fees
EU Internet Advocates Push Back Against Telecom “Fair-Share” Fees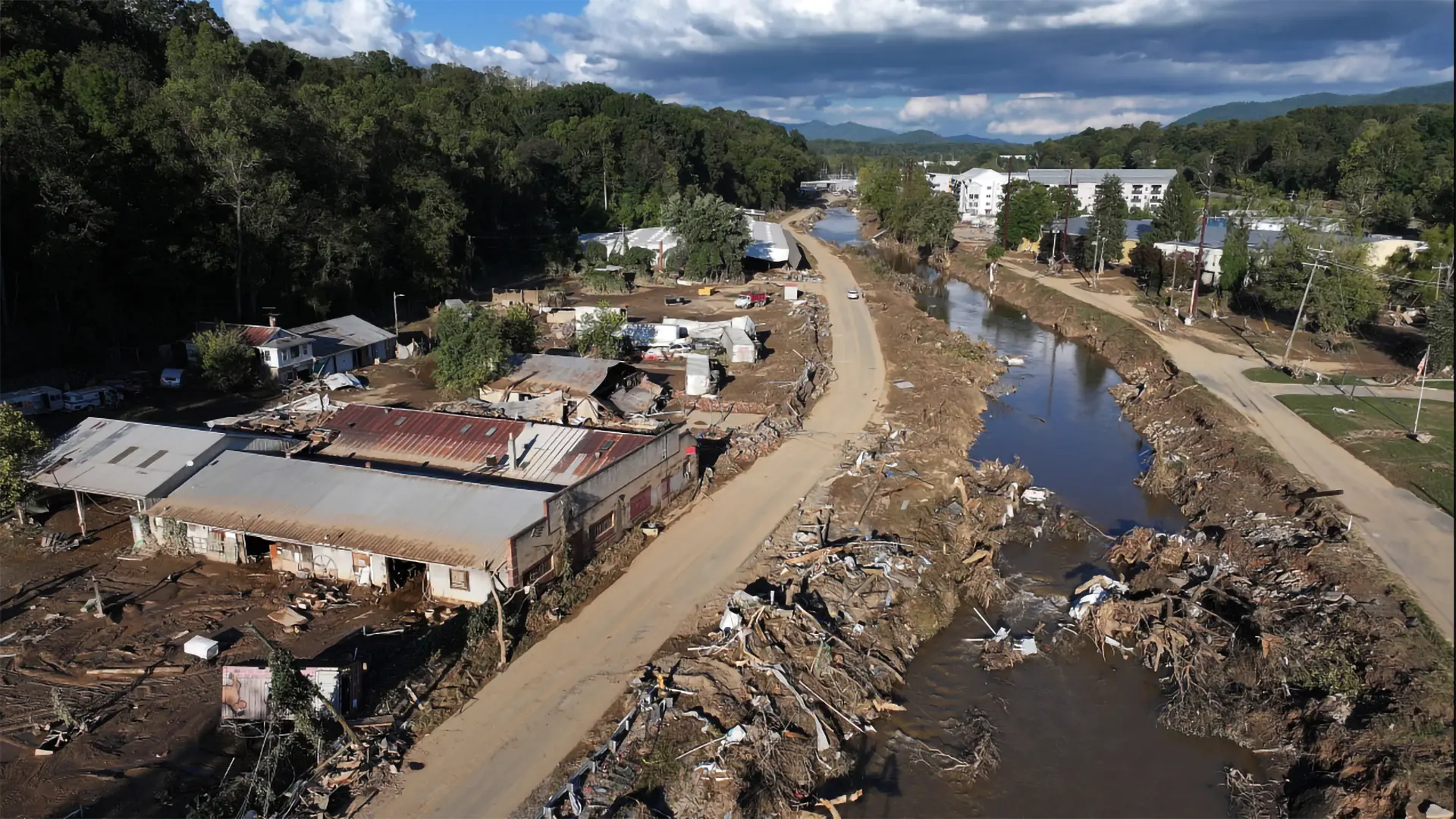 FCC Approves Starlink for Direct-to-Cell Service in Hurricane-Stricken North Carolina
FCC Approves Starlink for Direct-to-Cell Service in Hurricane-Stricken North Carolina Biden Administration Probes Chinese Telecom Firms Over U.S. Data Security Concerns
Biden Administration Probes Chinese Telecom Firms Over U.S. Data Security Concerns Ukraine’s Leading Mobile Operator Struck by War’s Largest Cyberattack
Ukraine’s Leading Mobile Operator Struck by War’s Largest Cyberattack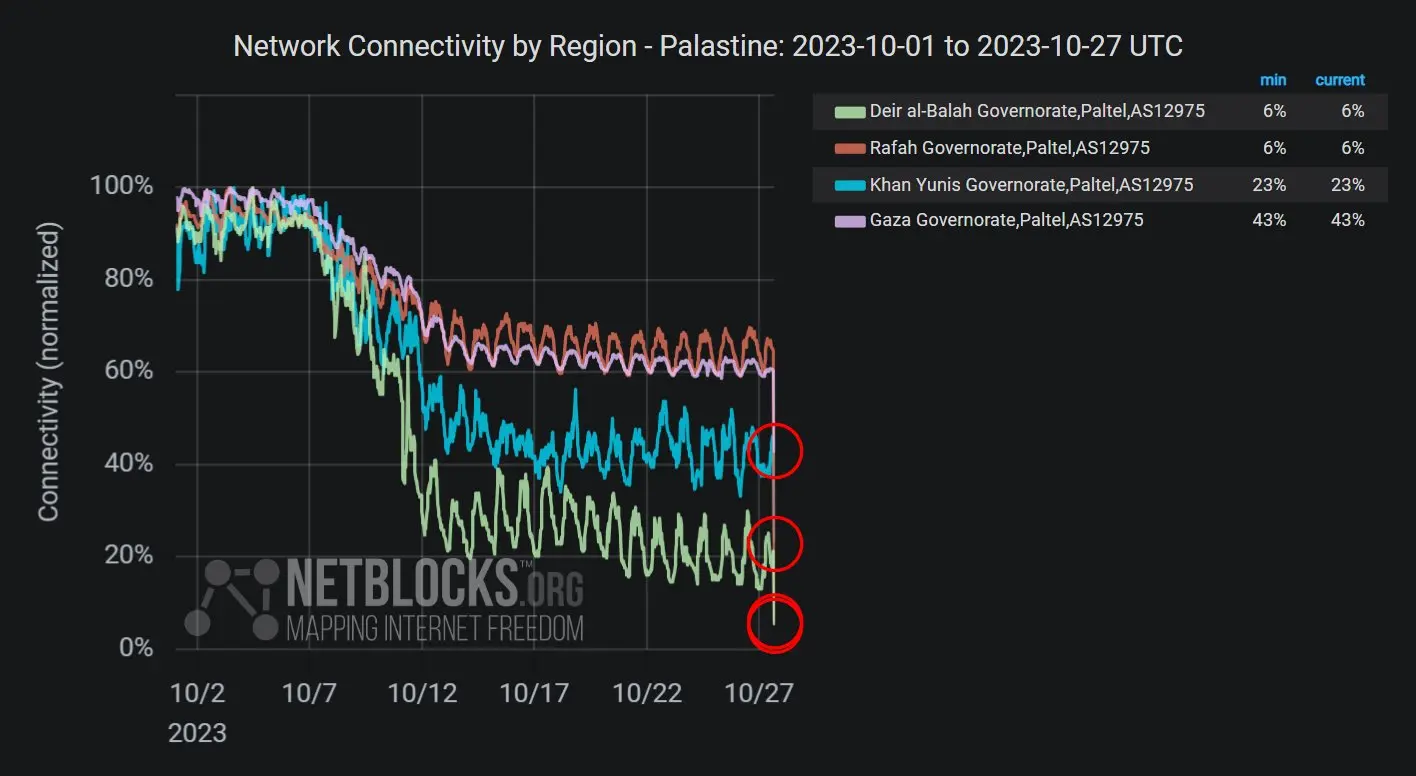 Gaza Plunges into Near-Total Internet and Cellular Blackout Amid Intensified Israeli Strikes
Gaza Plunges into Near-Total Internet and Cellular Blackout Amid Intensified Israeli Strikes SpaceX Quietly Launches New Website for Cellular Starlink Service
SpaceX Quietly Launches New Website for Cellular Starlink Service