

 Exploding internet traffic and AI demand are driving a rapid upgrade in fibre transport lasers, from early one gigabit systems to 400, 800 and even 1.6 terabit links reshaping backbone capacity worldwide as networks scale.
Exploding internet traffic and AI demand are driving a rapid upgrade in fibre transport lasers, from early one gigabit systems to 400, 800 and even 1.6 terabit links reshaping backbone capacity worldwide as networks scale.
 Despite steady expansion of fibre networks, the cost of building them is rising. New survey data show labour-heavy construction, higher aerial costs and persistent inflation pressures likely to push deployment expenses higher in 2026.
Despite steady expansion of fibre networks, the cost of building them is rising. New survey data show labour-heavy construction, higher aerial costs and persistent inflation pressures likely to push deployment expenses higher in 2026.
 An FCC ruling in a dispute between Comcast and Appalachian Power clarifies pole attachment cost rules, but exposes how regulatory delays and uncooperative utilities can slow fiber deployment and raise costs for broadband providers.
An FCC ruling in a dispute between Comcast and Appalachian Power clarifies pole attachment cost rules, but exposes how regulatory delays and uncooperative utilities can slow fiber deployment and raise costs for broadband providers.
 America has declared its intent to win the 6G race, casting next-generation wireless as vital to security and growth. Yet standards are global, vendors multinational, and the rhetoric looks like spectrum lobbying than technological rivalry.
America has declared its intent to win the 6G race, casting next-generation wireless as vital to security and growth. Yet standards are global, vendors multinational, and the rhetoric looks like spectrum lobbying than technological rivalry.
 Pew Research finds most Americans are online, yet access still tracks income, age and geography. Broadband gaps persist as subsidies fade, while smartphone dependence rises, reshaping how millions connect to work, services and civic life.
Pew Research finds most Americans are online, yet access still tracks income, age and geography. Broadband gaps persist as subsidies fade, while smartphone dependence rises, reshaping how millions connect to work, services and civic life.
 SpaceX has filed a plan to place more than a million satellites in low Earth orbit, recasting data centres as spaceborne infrastructure while testing regulators, safety, competition and the line between vision and paper ambition.
SpaceX has filed a plan to place more than a million satellites in low Earth orbit, recasting data centres as spaceborne infrastructure while testing regulators, safety, competition and the line between vision and paper ambition.
 Starlink is leveraging its growing dominance with data-hungry AI ambitions, regulatory demands, and space infrastructure plans. A merger with xAI could solidify its position as an unregulated gatekeeper of orbital connectivity and intelligence.
Starlink is leveraging its growing dominance with data-hungry AI ambitions, regulatory demands, and space infrastructure plans. A merger with xAI could solidify its position as an unregulated gatekeeper of orbital connectivity and intelligence.
 Low Earth Orbit satellite networks are dismantling traditional IP address allocation models. As signals defy borders, Regional Internet Registries face challenges in geolocation accuracy, routing security, and the definition of digital territory itself.
Low Earth Orbit satellite networks are dismantling traditional IP address allocation models. As signals defy borders, Regional Internet Registries face challenges in geolocation accuracy, routing security, and the definition of digital territory itself.
 Starlink expanded to 42 new countries in 2025, added 2.7 million customers, improved network speeds and latency, and continued satellite launches as it nears its first-phase constellation goal of 12,000 satellites.
Starlink expanded to 42 new countries in 2025, added 2.7 million customers, improved network speeds and latency, and continued satellite launches as it nears its first-phase constellation goal of 12,000 satellites.
 As AI shifts from experimentation to real-world deployment, its unseen foundation - undersea cables - emerges as a strategic frontier. Their resilience may shape not only infrastructure policy but the outcome of US-China AI competition.
As AI shifts from experimentation to real-world deployment, its unseen foundation - undersea cables - emerges as a strategic frontier. Their resilience may shape not only infrastructure policy but the outcome of US-China AI competition.
 Global internet use has surpassed six billion users, yet stark divides persist between regions, genders and urban-rural populations. Meanwhile, download speeds have surged and smartphones now dominate how people access the web worldwide.
Global internet use has surpassed six billion users, yet stark divides persist between regions, genders and urban-rural populations. Meanwhile, download speeds have surged and smartphones now dominate how people access the web worldwide.
 What began as an emergency response evolved into critical wartime infrastructure. Ukraine's experience with Starlink reveals the strategic risks and benefits of relying on privately operated networks for national resilience and defence.
What began as an emergency response evolved into critical wartime infrastructure. Ukraine's experience with Starlink reveals the strategic risks and benefits of relying on privately operated networks for national resilience and defence.
 Grenada advances its digital resilience by signing the Convention on the Packet Clearing House Organization, positioning itself to help shape global Internet governance while gaining coordinated support, stronger infrastructure, and a formal voice in decisions that influence worldwide connectivity and security.
Grenada advances its digital resilience by signing the Convention on the Packet Clearing House Organization, positioning itself to help shape global Internet governance while gaining coordinated support, stronger infrastructure, and a formal voice in decisions that influence worldwide connectivity and security.
 CaribNOG and PCH have renewed their partnership to boost the Caribbean's Internet resilience, expanding technical capacity, advancing inclusive training, and strengthening the people and systems essential for recovery as islands rebuild after Hurricane Melissa.
CaribNOG and PCH have renewed their partnership to boost the Caribbean's Internet resilience, expanding technical capacity, advancing inclusive training, and strengthening the people and systems essential for recovery as islands rebuild after Hurricane Melissa.
 Despite its promise of universal access, Starlink often fails to meet broadband benchmarks across key markets. New data reveals fluctuating performance and raises questions about reliability, digital equity, and tiered service models.
Despite its promise of universal access, Starlink often fails to meet broadband benchmarks across key markets. New data reveals fluctuating performance and raises questions about reliability, digital equity, and tiered service models.
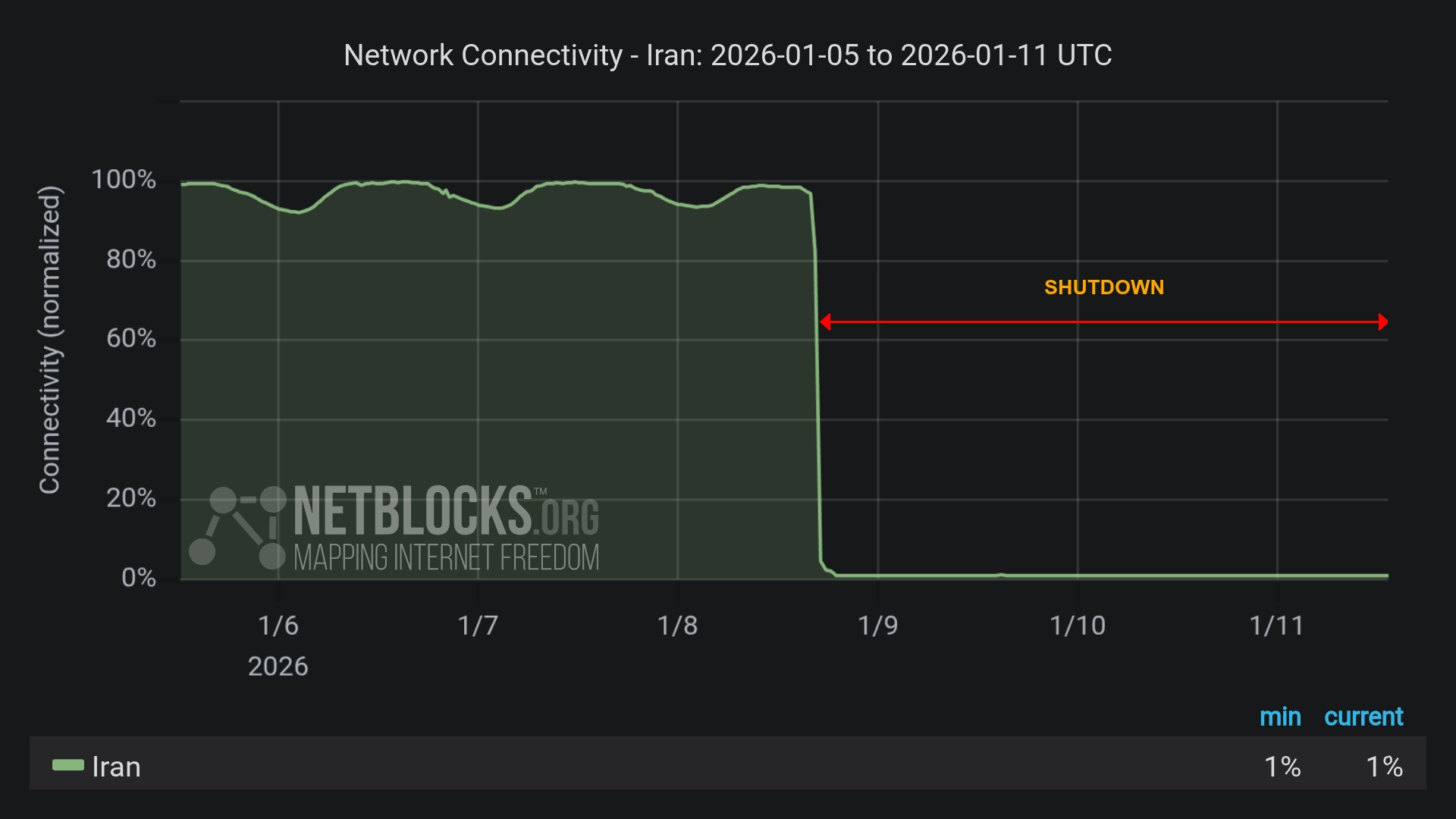 Iran Cuts Off Internet Nationwide as Regime Disrupts Even Starlink Amid Expanding Protests
Iran Cuts Off Internet Nationwide as Regime Disrupts Even Starlink Amid Expanding Protests US Senators Move to Shield Undersea Internet Cables from Global Threats
US Senators Move to Shield Undersea Internet Cables from Global Threats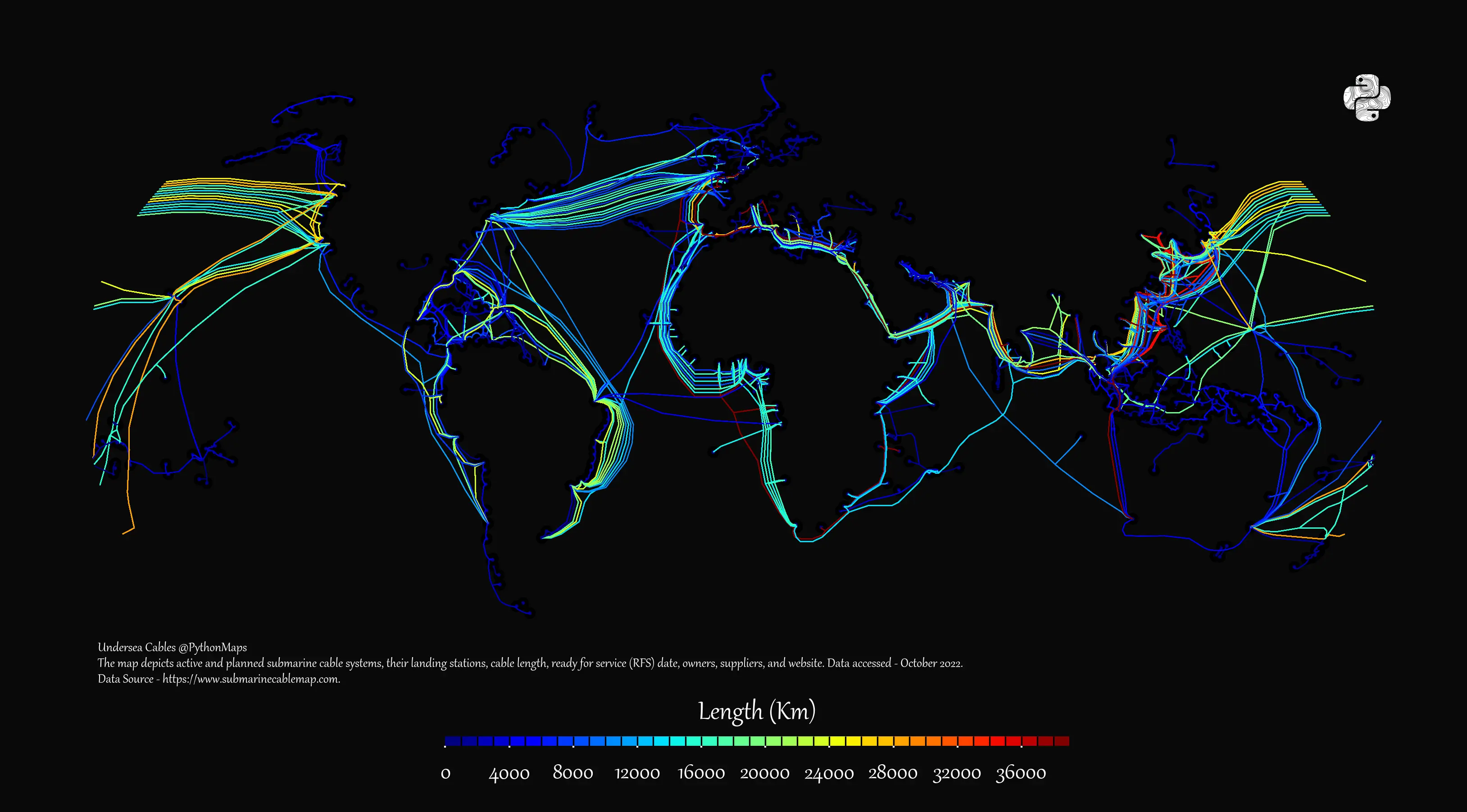 AI Boom Spurs Record Investment in Undersea Cables Amid Geopolitical and Security Concerns
AI Boom Spurs Record Investment in Undersea Cables Amid Geopolitical and Security Concerns Verizon and AWS Expand Network Ties to Meet AI Data Demands
Verizon and AWS Expand Network Ties to Meet AI Data Demands Starlink Passes 10,000 Satellites, Expanding Global Internet Reach
Starlink Passes 10,000 Satellites, Expanding Global Internet Reach JetBlue Selects Amazon’s Project Kuiper for In-Flight Satellite Connectivity
JetBlue Selects Amazon’s Project Kuiper for In-Flight Satellite Connectivity America’s Broadband Blind Spot: Audit Reveals Millions More Offline Than FCC Reports
America’s Broadband Blind Spot: Audit Reveals Millions More Offline Than FCC Reports Lack of Broadband Competition Leads to Higher Prices in Most U.S. Counties
Lack of Broadband Competition Leads to Higher Prices in Most U.S. Counties Meta’s Undersea Ambitions: A Cable to Power the AI Future
Meta’s Undersea Ambitions: A Cable to Power the AI Future Baltic Sea Infrastructure Targeted Amid Rising Geopolitical Tensions
Baltic Sea Infrastructure Targeted Amid Rising Geopolitical Tensions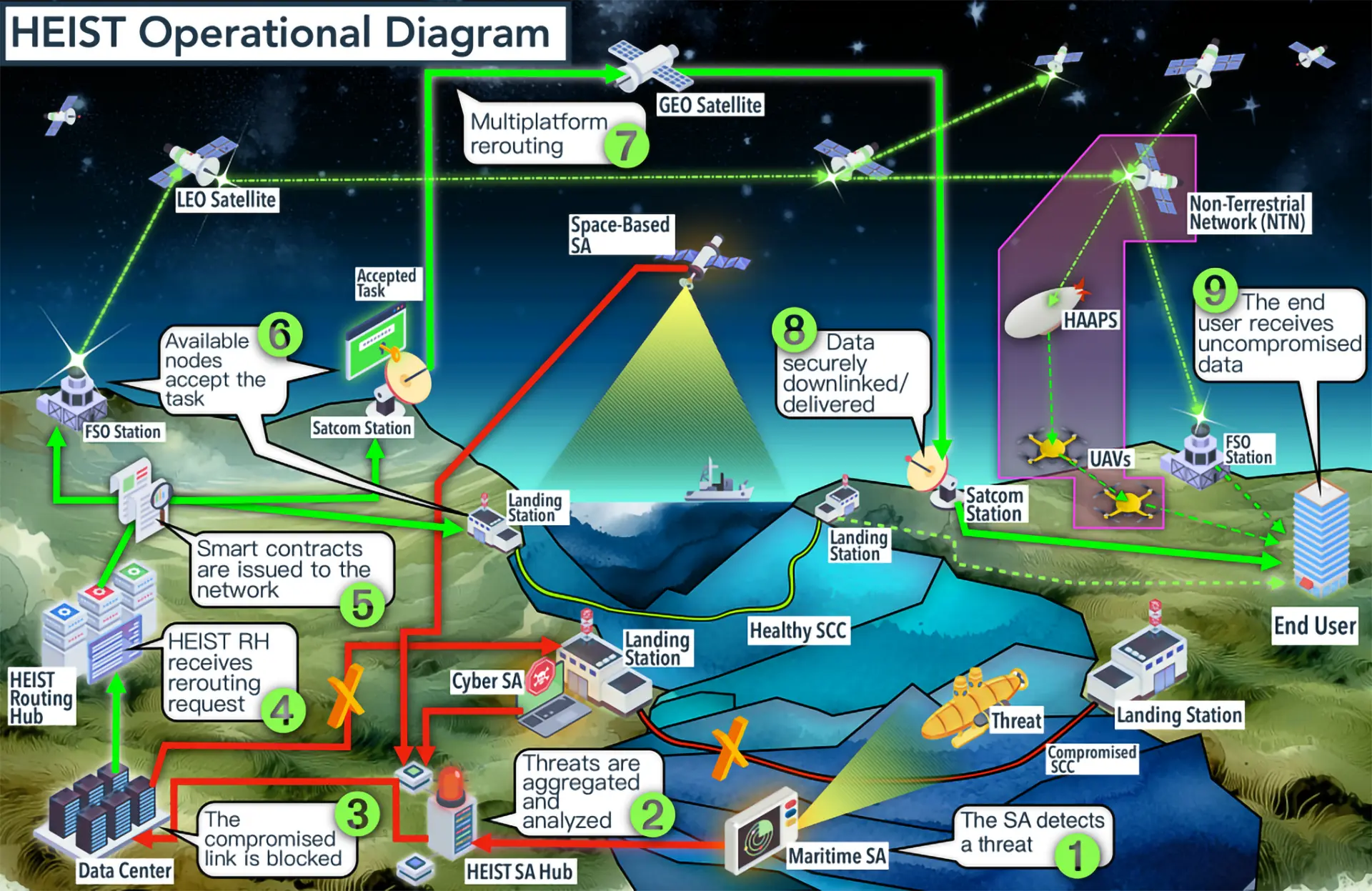 NATO’s Orbital Lifeline: A Backup Plan for the Internet
NATO’s Orbital Lifeline: A Backup Plan for the Internet Europe Seeks Space Independence with €10.6bn Iris² Satellite Network
Europe Seeks Space Independence with €10.6bn Iris² Satellite Network Meta’s $10 Billion Plan to Build the World’s Largest Subsea Cable Network
Meta’s $10 Billion Plan to Build the World’s Largest Subsea Cable Network EU Internet Advocates Push Back Against Telecom “Fair-Share” Fees
EU Internet Advocates Push Back Against Telecom “Fair-Share” Fees FCC Approves Starlink for Direct-to-Cell Service in Hurricane-Stricken North Carolina
FCC Approves Starlink for Direct-to-Cell Service in Hurricane-Stricken North Carolina