

 Efforts to combat online piracy are pushing courts to weaponise the Internet's naming system. Turning DNS operators into enforcement agents may deliver quick takedowns, but risks collateral damage, jurisdictional conflict and long-term fragmentation of the Internet.
Efforts to combat online piracy are pushing courts to weaponise the Internet's naming system. Turning DNS operators into enforcement agents may deliver quick takedowns, but risks collateral damage, jurisdictional conflict and long-term fragmentation of the Internet.
 Generative AI has turned brand impersonation from a nuisance into an industrial-scale threat, eroding trust. As ICANN's 2026 round approaches, DotBrand domains promise a structural fix to spoofing that strategies failed to deliver in 2012.
Generative AI has turned brand impersonation from a nuisance into an industrial-scale threat, eroding trust. As ICANN's 2026 round approaches, DotBrand domains promise a structural fix to spoofing that strategies failed to deliver in 2012.
 At Munich's twin security gatherings, leaders warned that cyber conflict, transatlantic rifts and weaponised AI are pushing the rules-based order into a perilous transition, where deterrence falters, norms erode and digital sovereignty trumps multistakeholder ideals.
At Munich's twin security gatherings, leaders warned that cyber conflict, transatlantic rifts and weaponised AI are pushing the rules-based order into a perilous transition, where deterrence falters, norms erode and digital sovereignty trumps multistakeholder ideals.
 Poland thwarted a large-scale cyberattack on its energy grid without disruption, offering a rare case study in critical infrastructure resilience, decentralised energy governance, and the balancing act between openness and digital security.
Poland thwarted a large-scale cyberattack on its energy grid without disruption, offering a rare case study in critical infrastructure resilience, decentralised energy governance, and the balancing act between openness and digital security.
 As Internet governance fragments in 2026, authority shifts from open, multistakeholder forums to state-led security regimes, legal instruments, and alliance-based cooperation, challenging longstanding institutions and reshaping global norms through enforcement rather than consensus.
As Internet governance fragments in 2026, authority shifts from open, multistakeholder forums to state-led security regimes, legal instruments, and alliance-based cooperation, challenging longstanding institutions and reshaping global norms through enforcement rather than consensus.
 Despite deep geopolitical divides, the WSIS+20 outcome document was adopted by consensus, preserving a multistakeholder vision for the digital future while deferring controversial issues to a time more conducive to progress.
Despite deep geopolitical divides, the WSIS+20 outcome document was adopted by consensus, preserving a multistakeholder vision for the digital future while deferring controversial issues to a time more conducive to progress.
 The ICC's new cyber policy reframes Internet infrastructure as crucial to prosecuting atrocities, prompting DNS operators and network providers to grapple with emerging obligations around evidence, neutrality, and cooperation in international justice.
The ICC's new cyber policy reframes Internet infrastructure as crucial to prosecuting atrocities, prompting DNS operators and network providers to grapple with emerging obligations around evidence, neutrality, and cooperation in international justice.
 eco's topDNS initiative and AV-Test are publishing monthly reports to help ISPs detect and mitigate DNS abuse by analysing malware, phishing, and PUA trends, creating a long-term data foundation for industry-wide transparency.
eco's topDNS initiative and AV-Test are publishing monthly reports to help ISPs detect and mitigate DNS abuse by analysing malware, phishing, and PUA trends, creating a long-term data foundation for industry-wide transparency.
 The international community has long struggled with the challenge of translating international law into actionable norms and practices in cyberspace. The conclusion of the United Nations Open-Ended Working Group (OEWG) on the security of and in the use of information and communications technologies 2021-2025 marks a vital milestone in that ongoing process.
The international community has long struggled with the challenge of translating international law into actionable norms and practices in cyberspace. The conclusion of the United Nations Open-Ended Working Group (OEWG) on the security of and in the use of information and communications technologies 2021-2025 marks a vital milestone in that ongoing process.
 Tech developments saw less drama than trade and environmental shifts during Trump's first 100 days. Continuity, not abrupt change, defined his approach to AI and digital regulation. Only 9 of 139 executive orders (EOs) focused on tech. Trump's tech policy emphasised reviews and incremental shifts. Public consultations on AI, cybersecurity, and cryptocurrencies signal steady evolution over upheaval.
Tech developments saw less drama than trade and environmental shifts during Trump's first 100 days. Continuity, not abrupt change, defined his approach to AI and digital regulation. Only 9 of 139 executive orders (EOs) focused on tech. Trump's tech policy emphasised reviews and incremental shifts. Public consultations on AI, cybersecurity, and cryptocurrencies signal steady evolution over upheaval.
 Sometime by year-end, the UN General Assembly (UNGA) will vote on the proposed UN Convention Against Cybercrime. The treaty is opposed by most civil liberties organizations and Internet businesses, although the US position appears uncertain, mostly for reasons of foreign policy.
Sometime by year-end, the UN General Assembly (UNGA) will vote on the proposed UN Convention Against Cybercrime. The treaty is opposed by most civil liberties organizations and Internet businesses, although the US position appears uncertain, mostly for reasons of foreign policy.
 Cybersecurity and artificial intelligence were among the key topics at the 79th UN General Assembly (UNGA). UNGA's 1st Committee, responsible for disarmament and international security, concluded its negotiations in mid-November 2024. It discussed the 3rd Annual Progress Report (APR) of the Open-Ended Working Group (OEWG) and adopted a resolution that recommends, inter alia, the establishment of a new permanent cybersecurity mechanism within the UN system. Furthermore, it adopted two resolutions on autonomous weapon systems (AWS).
Cybersecurity and artificial intelligence were among the key topics at the 79th UN General Assembly (UNGA). UNGA's 1st Committee, responsible for disarmament and international security, concluded its negotiations in mid-November 2024. It discussed the 3rd Annual Progress Report (APR) of the Open-Ended Working Group (OEWG) and adopted a resolution that recommends, inter alia, the establishment of a new permanent cybersecurity mechanism within the UN system. Furthermore, it adopted two resolutions on autonomous weapon systems (AWS).
 In CSC's recent insight paper, we address the trend that many business leaders today don't realize the extent to which their modern enterprise -- and its millions of digital assets -- rely on. It's a vast domain ecosystem that needs to be protected from online threats. Often, to better understand this need for domain security, we need to understand how critical and interconnected domains are within a business.
In CSC's recent insight paper, we address the trend that many business leaders today don't realize the extent to which their modern enterprise -- and its millions of digital assets -- rely on. It's a vast domain ecosystem that needs to be protected from online threats. Often, to better understand this need for domain security, we need to understand how critical and interconnected domains are within a business.
 Despite global polarization, recent UN cyber diplomacy has achieved three significant agreements in 2024: a cyber attack reporting system, a convention against cybercrime, and a "Global Digital Compact." These successes show that consensus on global issues is possible, though the vague wording of agreements raises concerns about their long-term effectiveness in ensuring security and peace.
Despite global polarization, recent UN cyber diplomacy has achieved three significant agreements in 2024: a cyber attack reporting system, a convention against cybercrime, and a "Global Digital Compact." These successes show that consensus on global issues is possible, though the vague wording of agreements raises concerns about their long-term effectiveness in ensuring security and peace.
 Interisle Consulting Group today released its fourth annual Phishing Landscape report investigating where and how cybercriminals acquire naming and hosting resources for phishing. Our study shows that cybercriminals evolved their tactics for obtaining attack resources, including sharply increasing their exploitation of subdomain and gateway providers.
Interisle Consulting Group today released its fourth annual Phishing Landscape report investigating where and how cybercriminals acquire naming and hosting resources for phishing. Our study shows that cybercriminals evolved their tactics for obtaining attack resources, including sharply increasing their exploitation of subdomain and gateway providers.
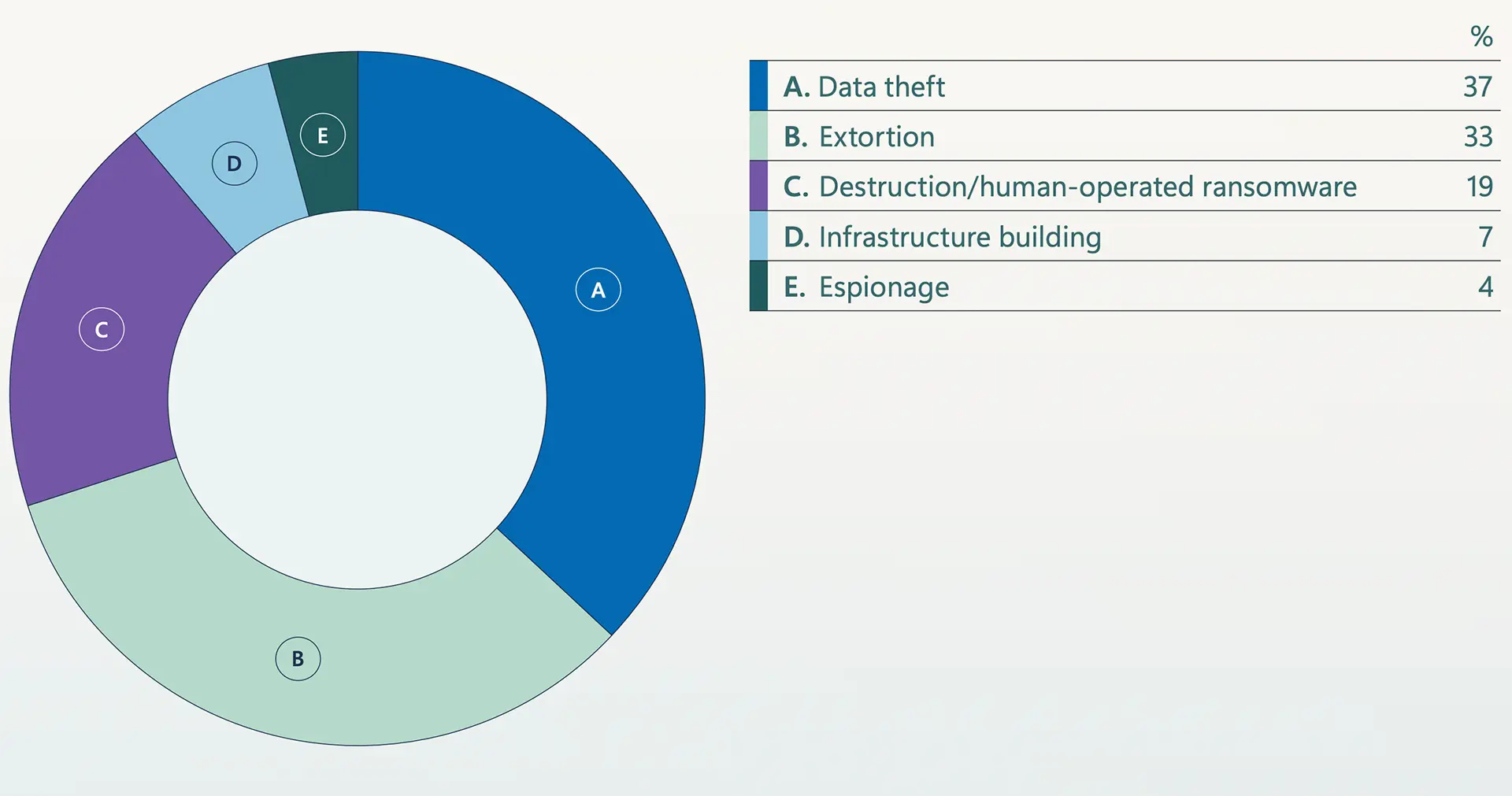 Microsoft Warns Extortion Drives Majority of Attacks Amid AI Escalation, Identity Collapse, and Global Fragmentation
Microsoft Warns Extortion Drives Majority of Attacks Amid AI Escalation, Identity Collapse, and Global Fragmentation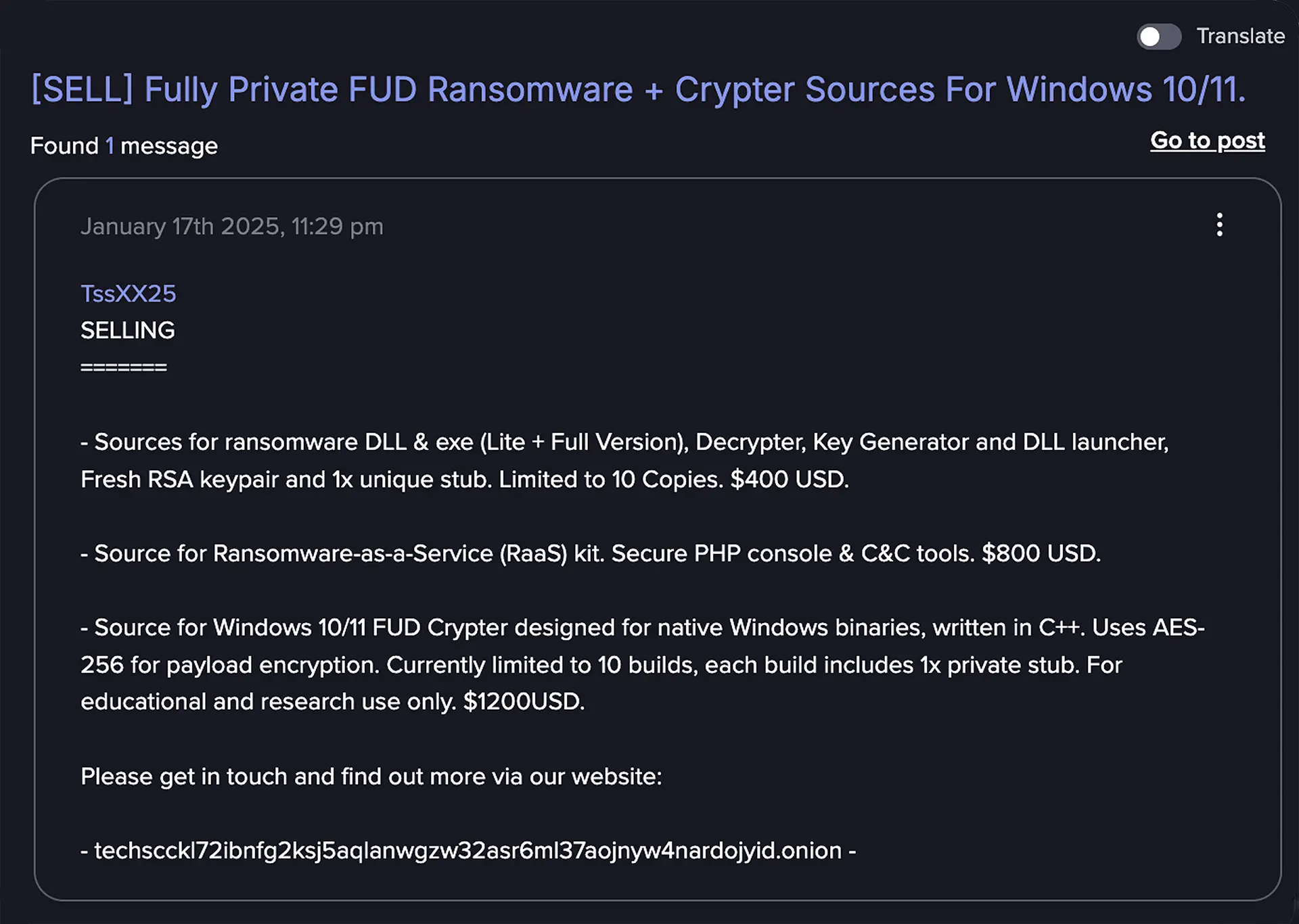 Advanced AI Is Reshaping the Cybercriminal Landscape at Alarming Speed
Advanced AI Is Reshaping the Cybercriminal Landscape at Alarming Speed INTERPOL Leads Arrest of 1,209 Suspects in Pan-African Cybercrime Crackdown, Recovers $97 Million
INTERPOL Leads Arrest of 1,209 Suspects in Pan-African Cybercrime Crackdown, Recovers $97 Million Cyberattacks Spur Boom in Insurance Demand Amid Rising Global Threats
Cyberattacks Spur Boom in Insurance Demand Amid Rising Global Threats India Launches ‘.bank.in’ and ‘.fin.in’ Domains to Deter Financial Fraud
India Launches ‘.bank.in’ and ‘.fin.in’ Domains to Deter Financial Fraud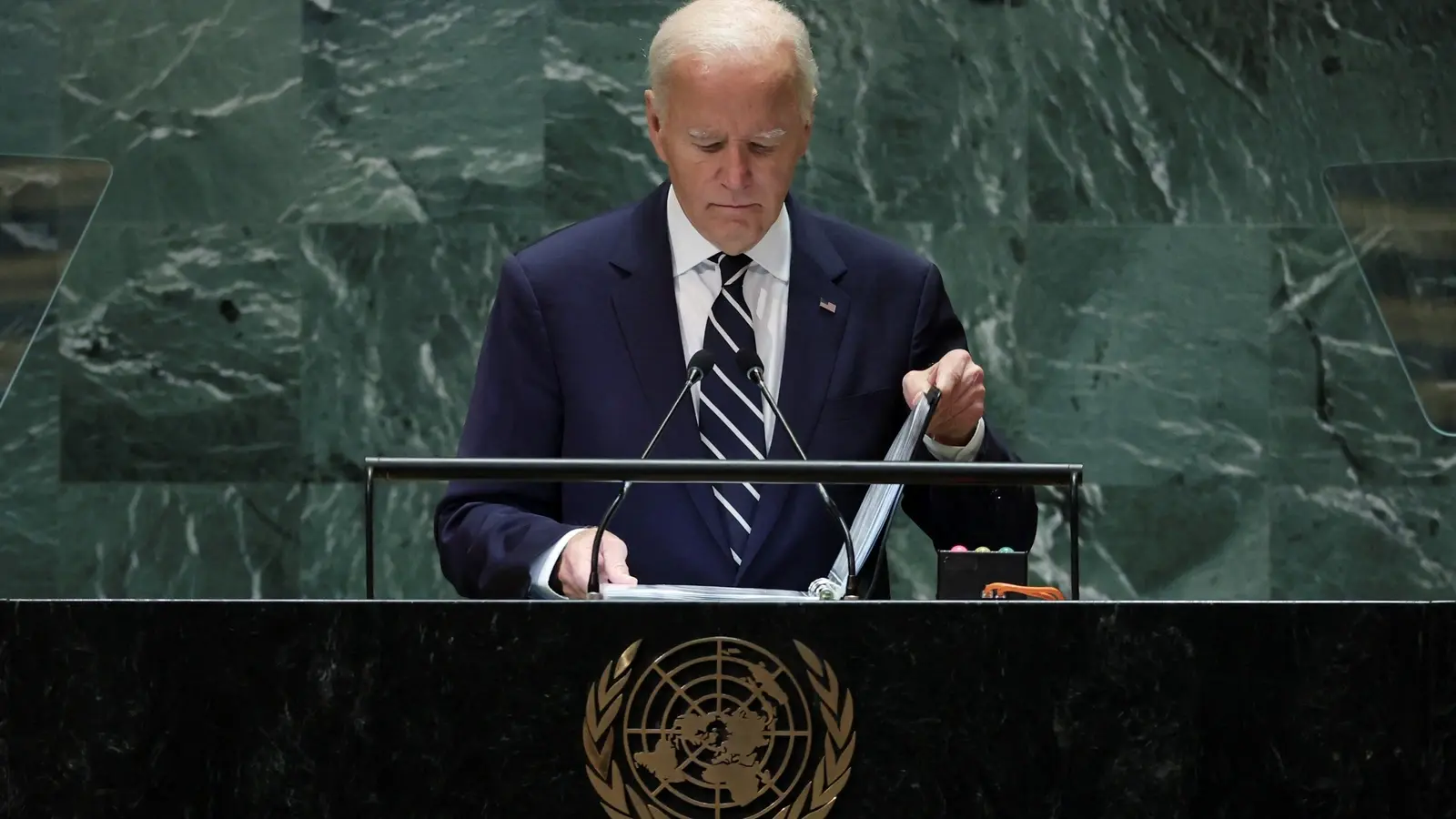 Biden Administration to Back UN Cybercrime Treaty Amid Controversy
Biden Administration to Back UN Cybercrime Treaty Amid Controversy Ransomware Crisis in U.S. Healthcare
Ransomware Crisis in U.S. Healthcare Global Law Enforcement Strikes Major Blow Against LockBit Ransomware Operation
Global Law Enforcement Strikes Major Blow Against LockBit Ransomware Operation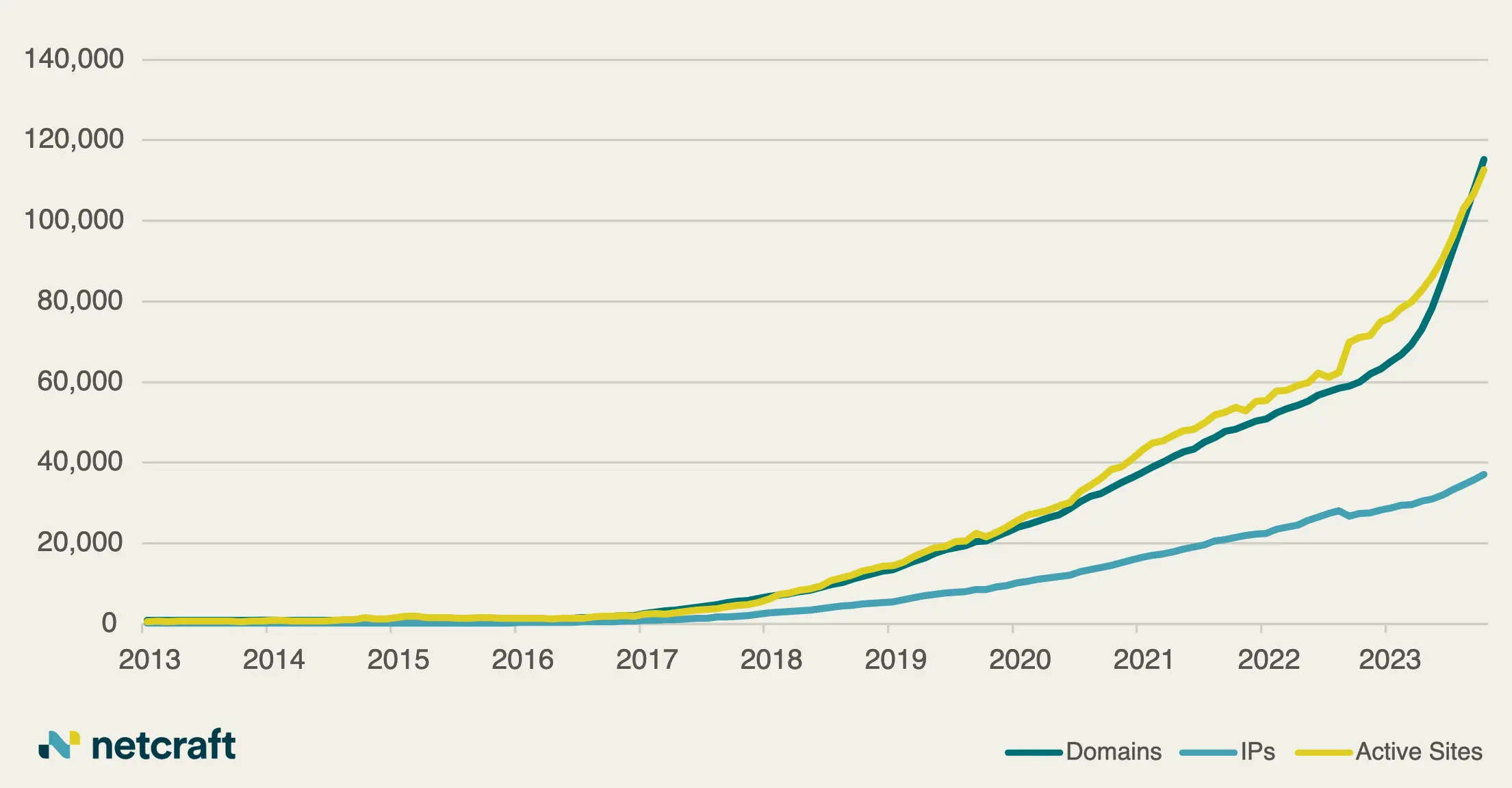 Rise in Cybercrime Exploiting Artificial Intelligence Hype Leads to Growing Threats Within the .ai Domain Space
Rise in Cybercrime Exploiting Artificial Intelligence Hype Leads to Growing Threats Within the .ai Domain Space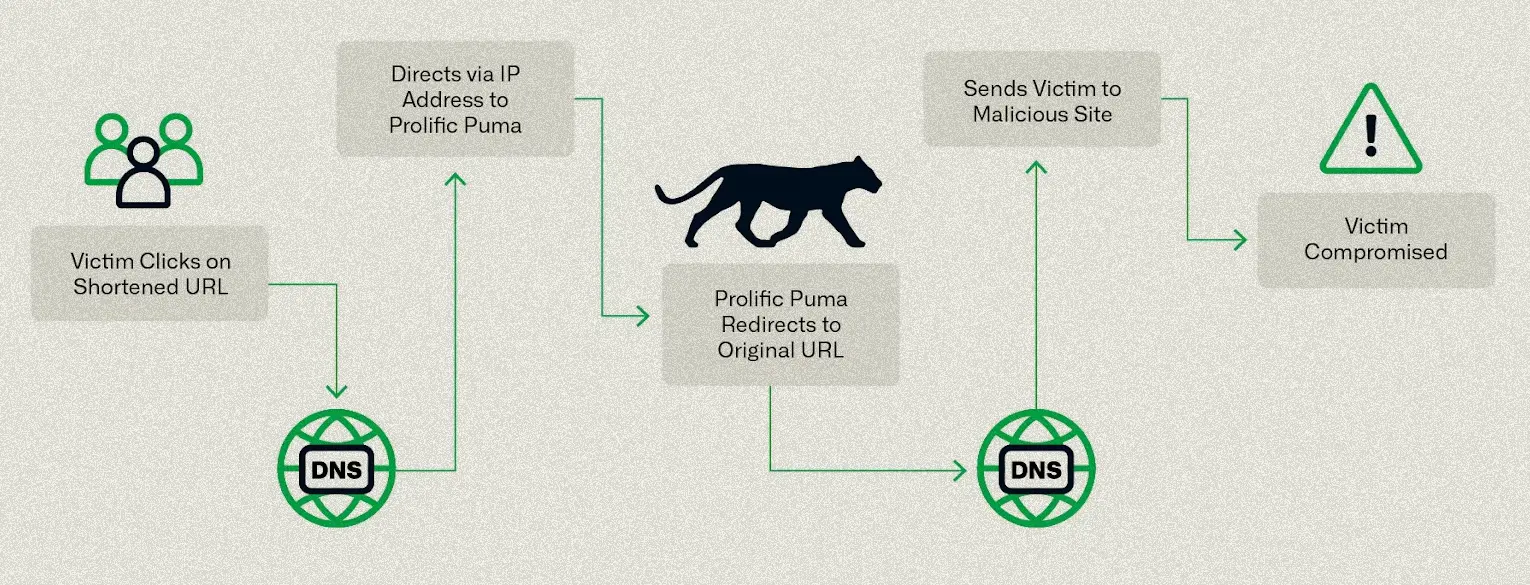 Researchers Uncover Massive Underground Link-Shortening Service Used by Malicious Actors
Researchers Uncover Massive Underground Link-Shortening Service Used by Malicious Actors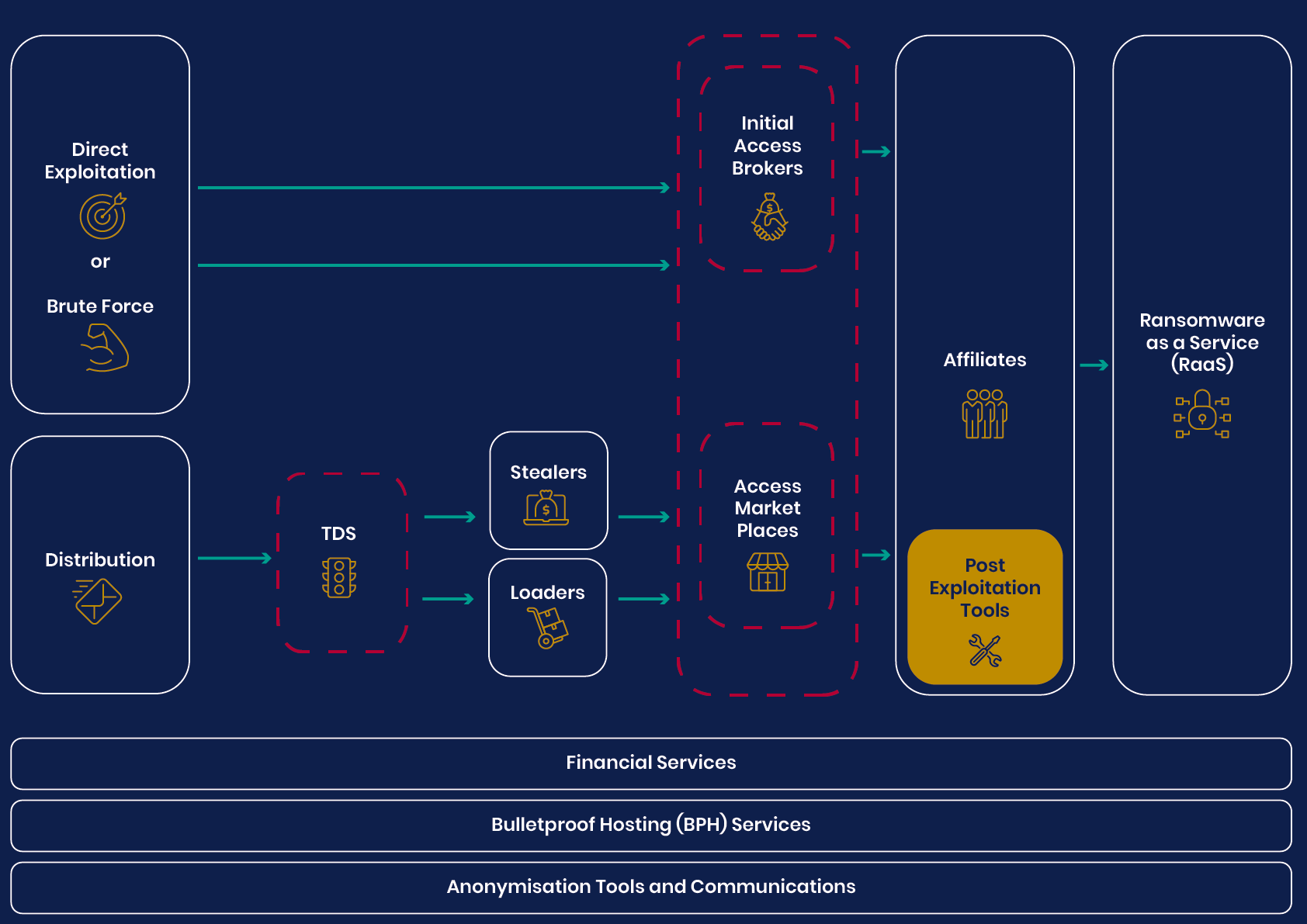 UK’s National Agencies Release White Paper on Evolving Cyber Crime Ecosystem
UK’s National Agencies Release White Paper on Evolving Cyber Crime Ecosystem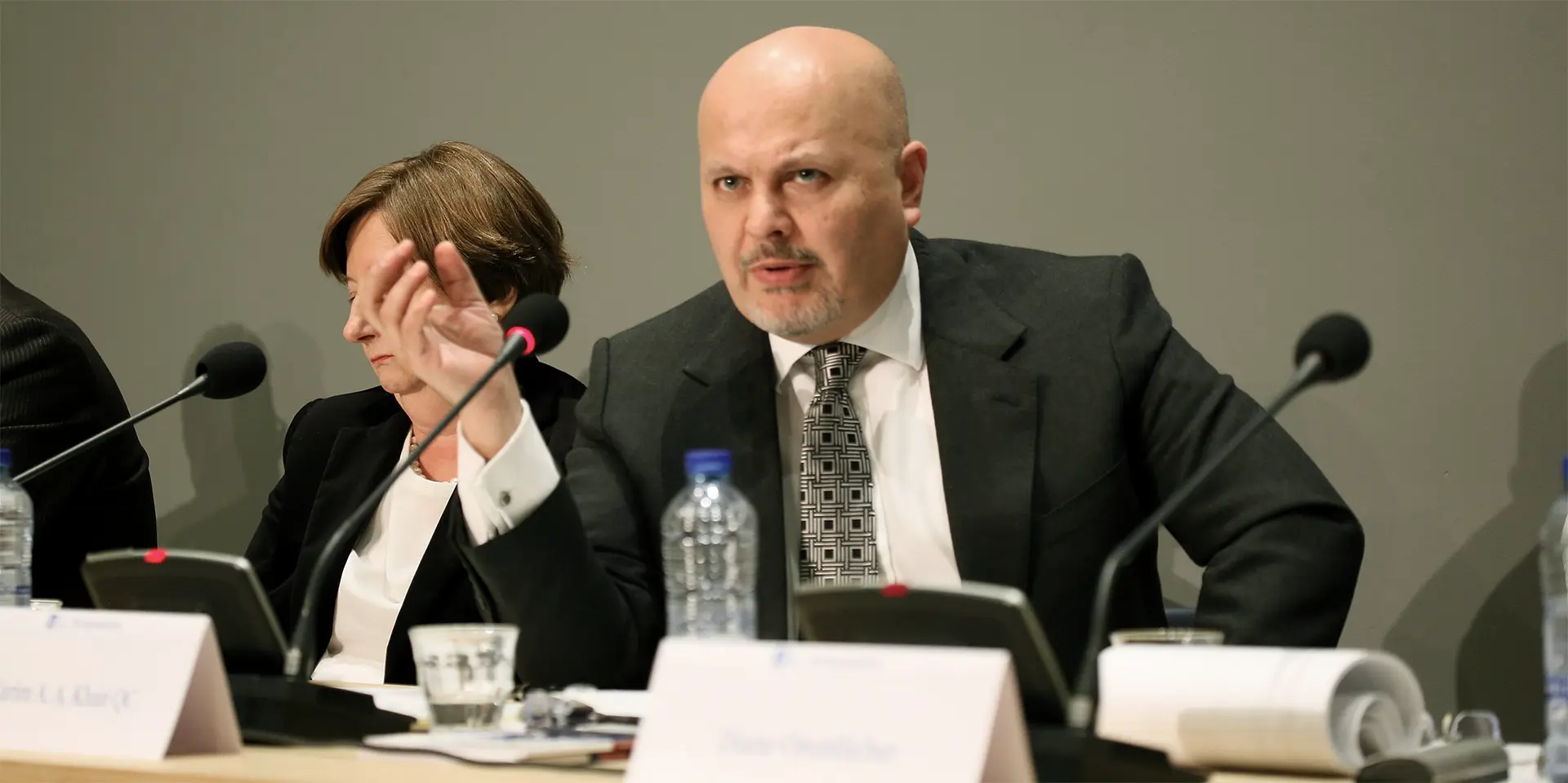 The Hague to Probe Cyberwarfare Under Existing International Law
The Hague to Probe Cyberwarfare Under Existing International Law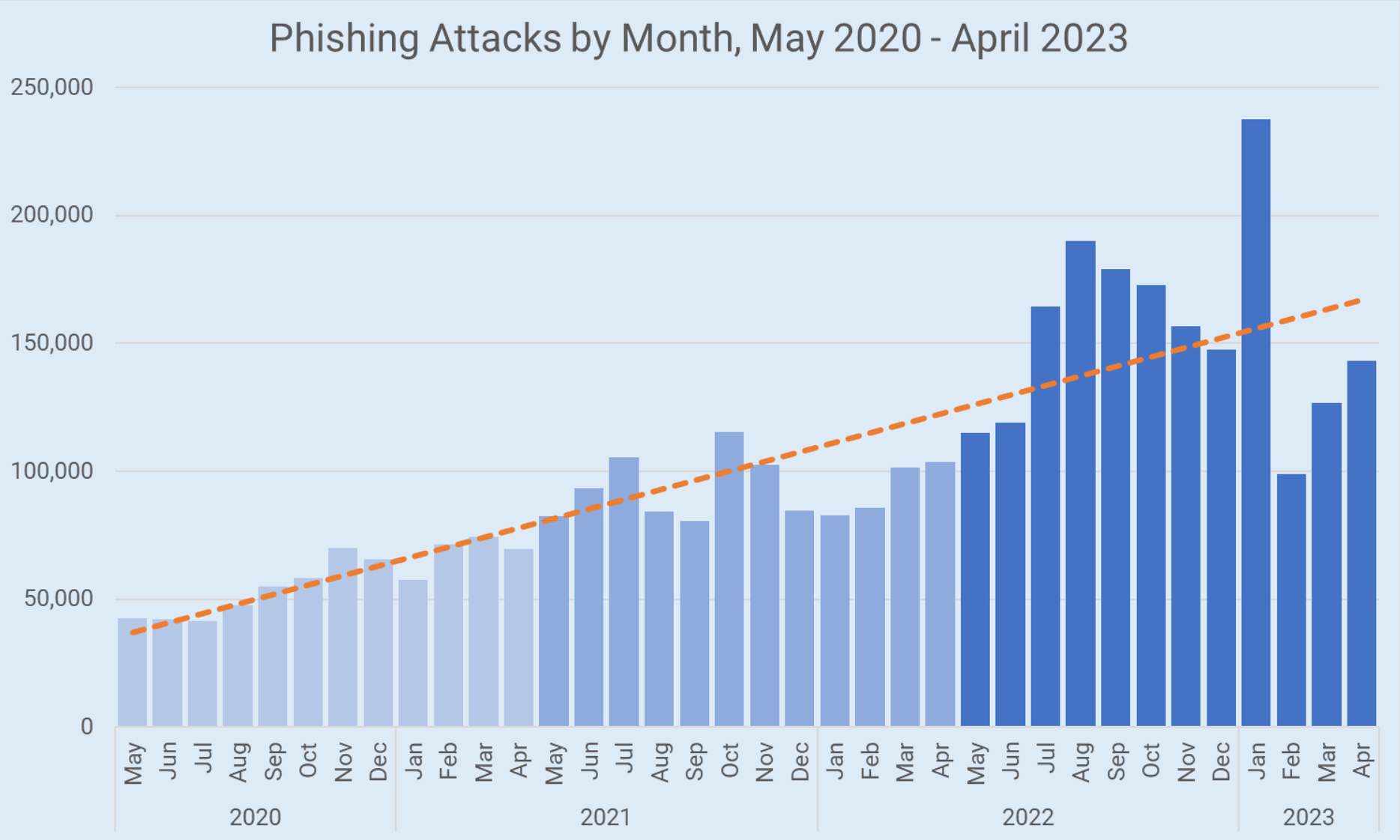 Phishing Attacks Surge Despite Increased Awareness, New Strategies Needed
Phishing Attacks Surge Despite Increased Awareness, New Strategies Needed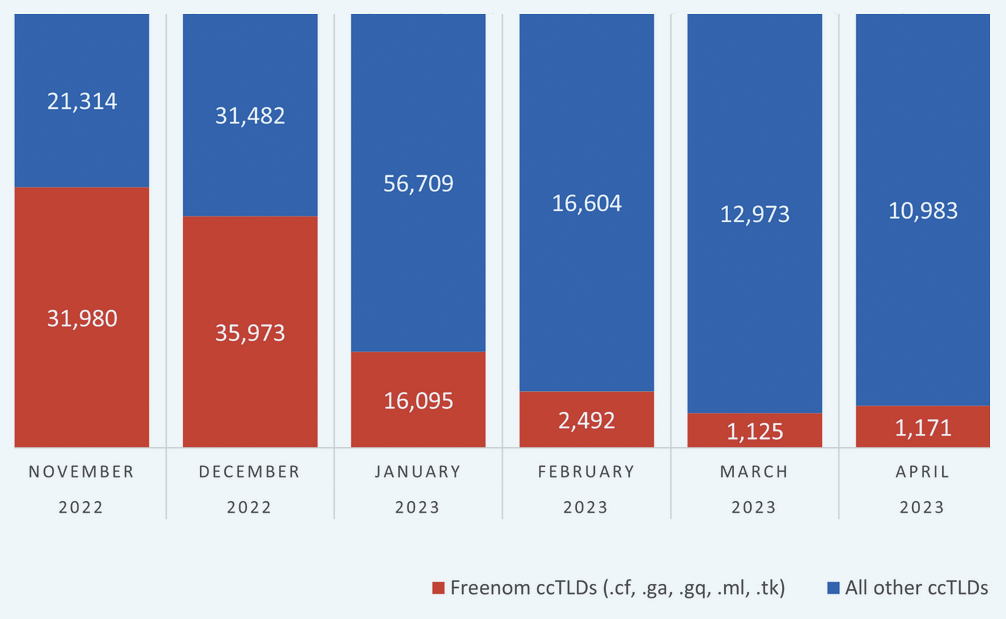 Meta Lawsuit Leads to Significant Decline in Phishing Domains Tied to Freenom
Meta Lawsuit Leads to Significant Decline in Phishing Domains Tied to Freenom Microsoft, Fortra, and Health-ISAC Take Legal Action Against the Abuse of Cobalt Strike to Combat Ransomware Attacks
Microsoft, Fortra, and Health-ISAC Take Legal Action Against the Abuse of Cobalt Strike to Combat Ransomware Attacks