


|
||
|
||
The Atomic Stealer, also known as “AMOS,” first emerged in September this year by spreading on Macs disguised as popular applications. This time around, it has been wreaking more havoc in the guise of a fake browser update dubbed “ClearFake.” To widen their victim base, the stealer’s operators compromised several websites for their illicit gain.
Malwarebytes Labs published a list of Atomic Stealer indicators of compromise (IoCs) along with their in-depth malware analysis earlier this November. To gather more information about the threat and identify other potential attack vectors that may not be public yet, we expanded the list of IoCs, specifically six domains and one IP address, and discovered:
A sample of the additional artifacts obtained from our analysis is available for download from our website.
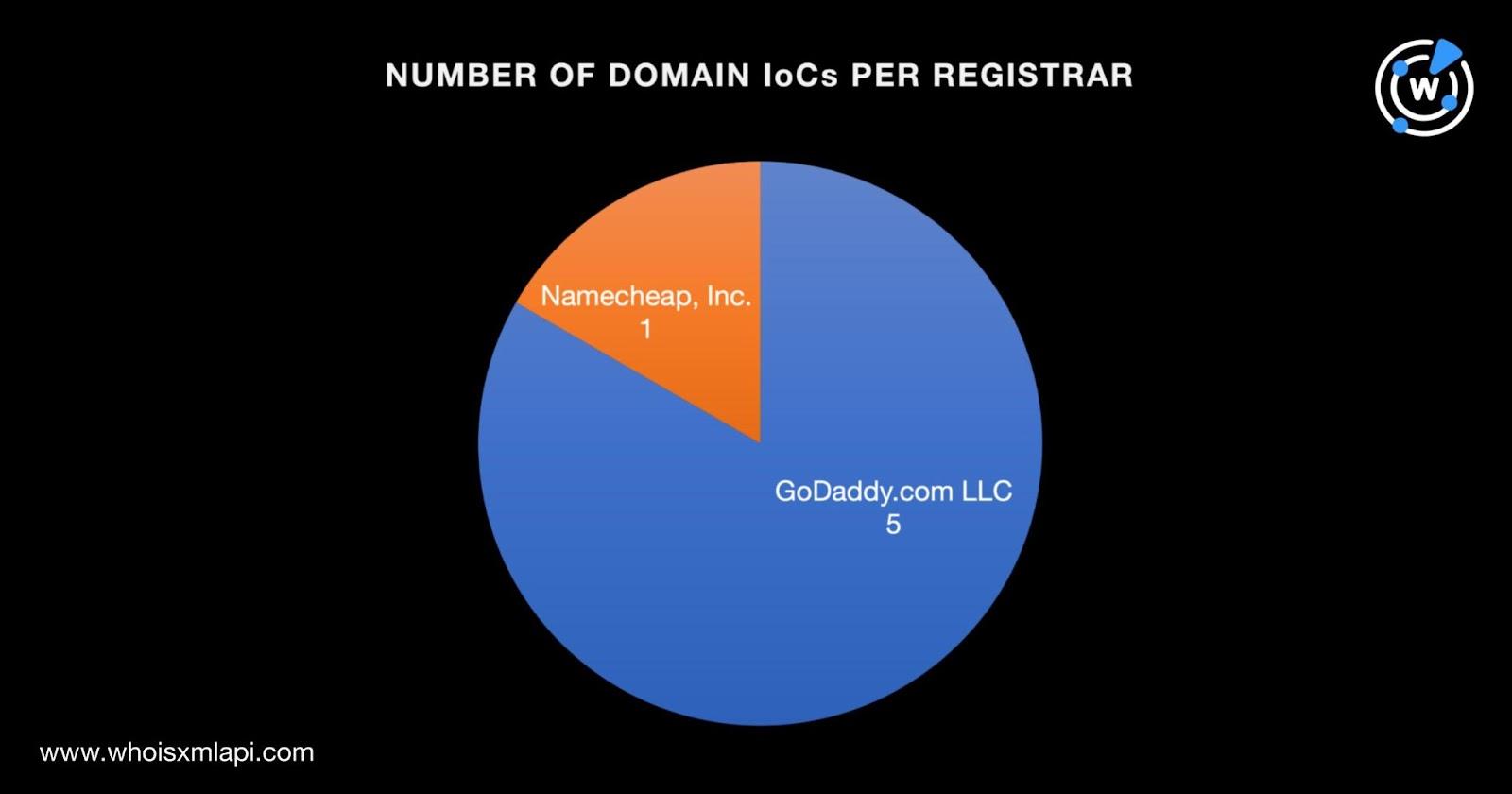
We first took a look at the six domains identified as IoCs via a bulk WHOIS lookup and found that:
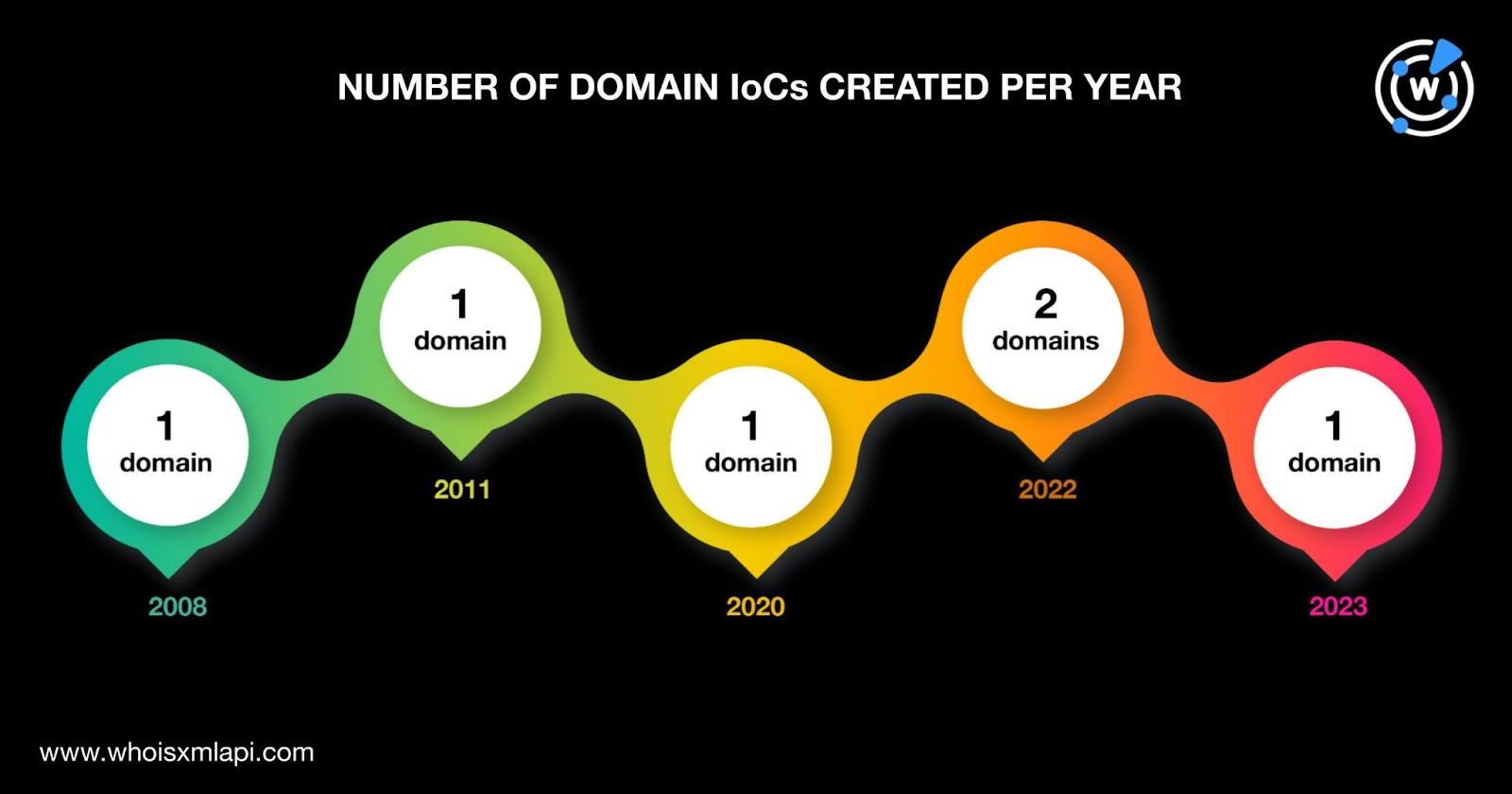
The six domains were created between 2008 and 2023—two in 2022 and one each in 2008, 2011, 2020, and 2023.
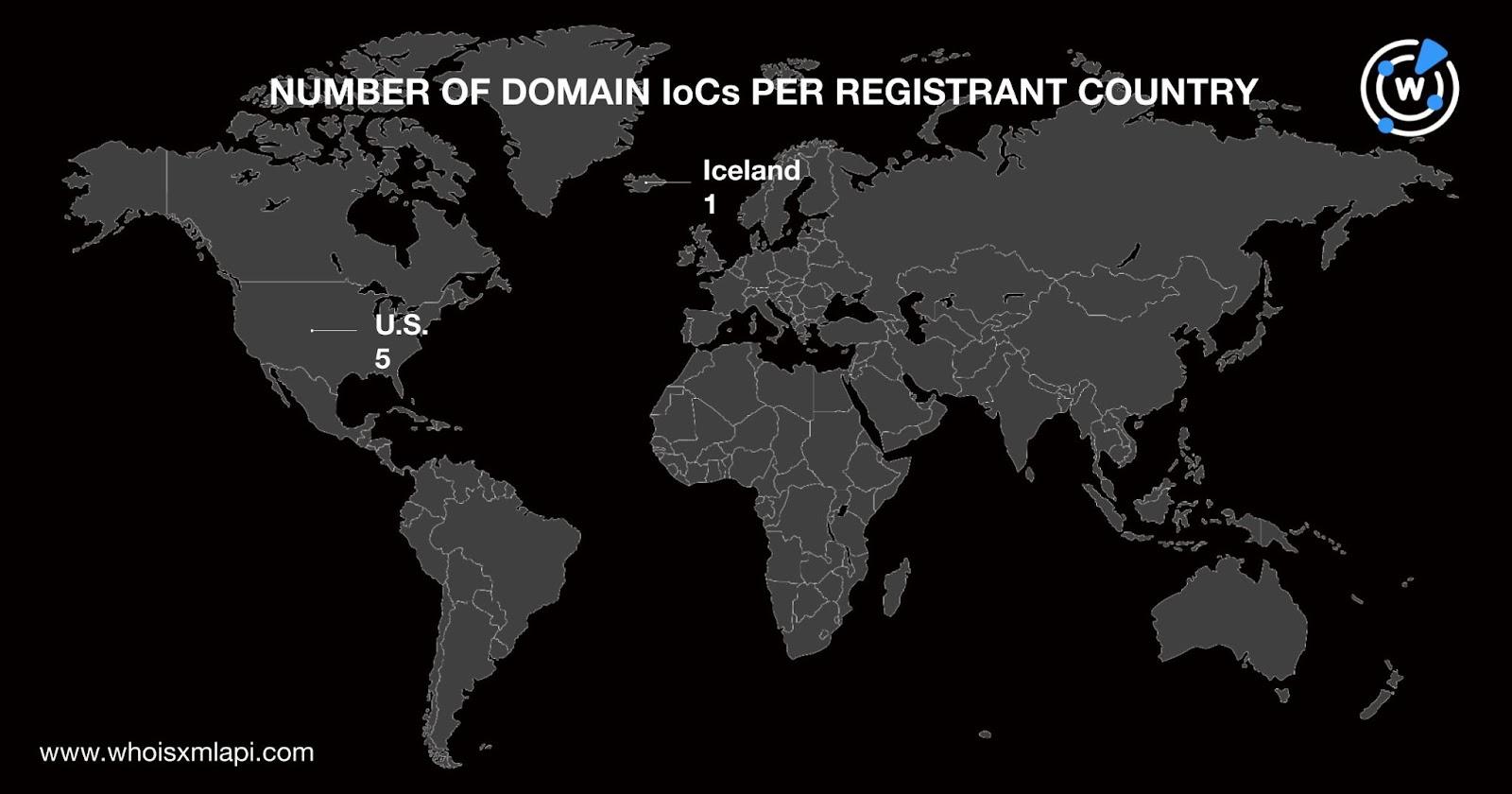
Five of the domains had the U.S. recorded as their registrant country, while one indicated Iceland.
Next, we subjected the IP address identified as an IoC to an IP geolocation lookup and found that:
We began our expansion analysis by performing WHOIS History Search queries on the six domains identified as Atomic Stealer IoCs. We uncovered 15 email addresses that appeared anywhere in their historical WHOIS records.
Reverse WHOIS Search queries on the seven public email addresses showed that four of them appeared in the current WHOIS records of 31 email-connected domains after duplicates and the IoCs were removed.
A closer look at the email-connected domains revealed that nine of them could be mimicking three Canadian organizations—Costco Wholesale Canada, the Royal Bank of Canada, and Scotiabank Canada—based on their text string usage summed up in the table below.
| EMAIL-CONNECTED DOMAIN | ORGANIZATION POSSIBLY BEING MIMICKED |
|---|---|
| canada-costco-redeem2percent[.]com | Costco Wholesale Canada |
| rbctrustroyalcanada[.]comtrustclientrbc[.]com | Royal Bank of Canada |
| canadascotia-sign-intrust[.]com scotiabank-sign-in[.]com scotiacatrust[.]com scotiaonline-client[.]com scotiatrustweb[.]com sign-intrust-scotiaonline[.]com | Scotiabank Canada |
The WHOIS records of the three organizations possibly being imitated had identifiable data points. WHOIS lookups for Costco Wholesale Canada’s and the Royal Bank of Canada’s official domains—costco[.]ca and rbcroyalbank[.]com, respectively—allowed us to determine their registrant email addresses. A WHOIS lookup for Scotiabank Canada’s official domain—scotiabank[.]com—meanwhile, enabled us to obtain its registrant organization.
In comparison, none of the nine email-connected domains’ WHOIS records contained the information detailed above. In fact, they all had heavily redacted WHOIS records. As such, none of them could be publicly attributed to the legitimate companies and may thus be considered typosquatting domains.
Next, we subjected the six domains identified as IoCs to DNS lookups and found that they resolved to seven unique IP addresses. Bulk IP geolocation lookups for them showed that:
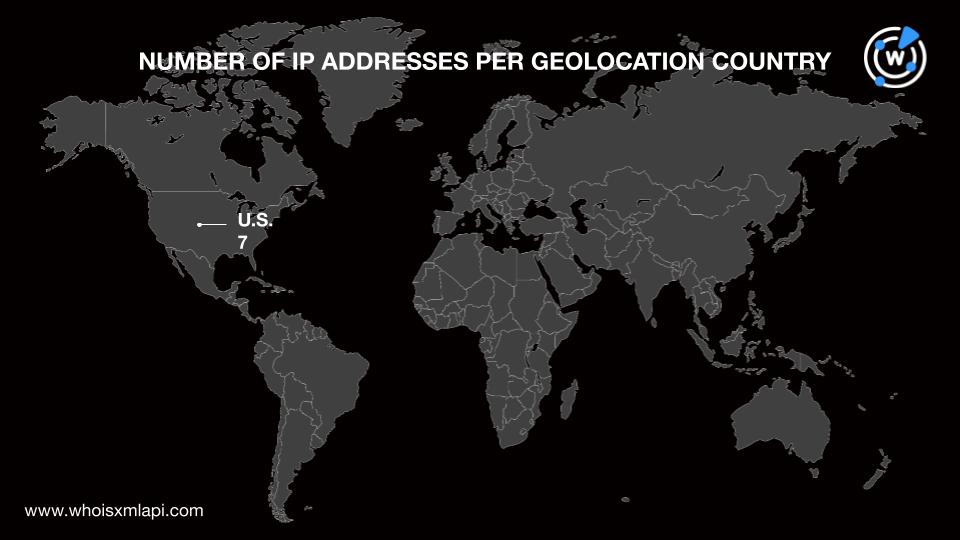
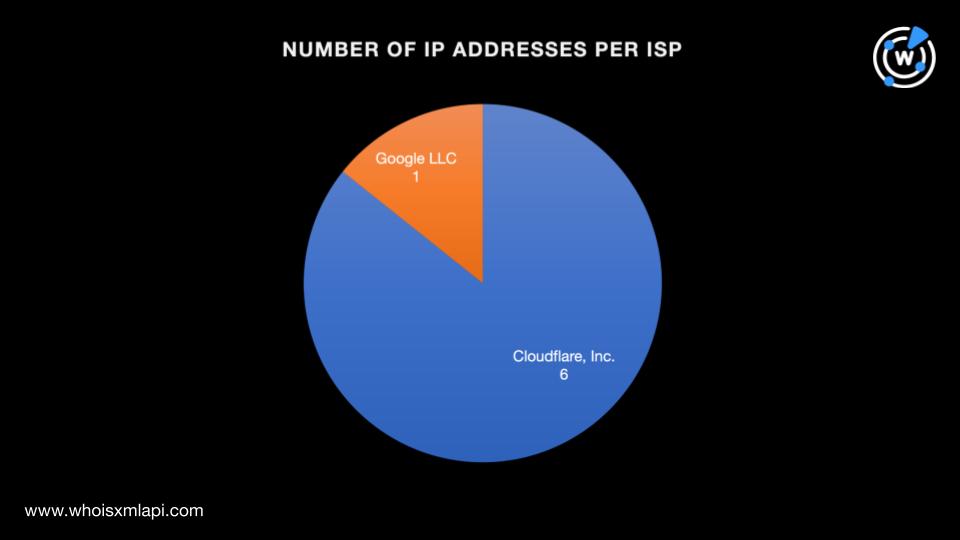
They were also spread across two ISPs led by Cloudflare, Inc. (six IP addresses). One IP address was administered by Google LLC.
Threat Intelligence Lookup also revealed that six of the IP addresses were associated with various threats. Take a look at our findings in the table below.
| IP ADDRESS | THREAT INTELLIGENCE LOOKUP FINDING |
|---|---|
| 104[.]21[.]43[.]174 | Associated with 8,149 threats |
| 104[.]21[.]49[.]159 | Associated with 8,171 threats |
| 104[.]21[.]30[.]25 | Associated with 8,176 threats |
| 172[.]67[.]182[.]141 | Associated with 8,271 threats |
| 172[.]67[.]147[.]71 | Associated with 8,195 threats |
| 172[.]67[.]150[.]110 | Associated with 8,196 threats |
We now had a total of eight IP addresses to work with after adding the one identified as an IoC. Our lookups also revealed that seven of the IP addresses could be shared hosts and one didn’t have active resolutions.
As the final step in our search for connected web properties registered in the past decade or so, we looked for domains and subdomains that contained the text strings found among the six domains identified as IoCs below via Domains & Subdomains Discovery. We found 17 domains and 14 subdomains.
| TEXT STRINGS FOUND AMONG THE DOMAINS IDENTIFIED AS IoCs | NUMBER OF DOMAINS FOUND USING DOMAINS & SUBDOMAINS DISCOVERY | NUMBER OF SUBDOMAINS FOUND USING DOMAINS & SUBDOMAINS DISCOVERY |
|---|---|---|
| thebestthings1337 | 1 | 0 |
| chalomannoakhali | 1 | 0 |
| jaminzaidad | 4 | 2 |
| royaltrustrbc | 2 | 0 |
| wifi-ber | 9 | 12 |
After removing duplicates, the domains already identified as IoCs, and the email- and IP-connected domains, we were left with 12 and 14 string-connected domains and subdomains, respectively.
Interestingly, one string-connected domain—royaltrustrbc[.]online—could be cybersquatting on the Royal Bank of Canada. Like the potential typosquatting domains we found earlier, royaltrustrbc[.]online could not be publicly attributed to the bank. Its WHOIS record did not list the Royal Bank of Canada’s registrant email address either.
Our peek under the hood of the Atomic Stealer’s infrastructure led to the discovery of 64 potentially connected artifacts that have not been published in other reports. Part of that list are domains that could figure as attack vectors in phishing campaigns targeting Costco Wholesale Canada, the Royal Bank of Canada, and Scotiabank Canada.
If you wish to perform a similar investigation or learn more about the products used in this research, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Disclaimer: We take a cautionary stance toward threat detection and aim to provide relevant information to help protect against potential dangers. Consequently, it is possible that some entities identified as “threats” or “malicious” may eventually be deemed harmless upon further investigation or changes in context. We strongly recommend conducting supplementary investigations to corroborate the information provided herein.
Sponsored byWhoisXML API

Sponsored byCSC

Sponsored byIPv4.Global

Sponsored byRadix

Sponsored byDNIB.com

Sponsored byVerisign

Sponsored byVerisign
