


|
||
|
||
It’s not unusual for threat actors to pick up after fellow cyber attackers shut down their operations. Many of them still want to cause as much trouble without having to start from scratch—building their own malicious creations and infrastructure.
That is the story of phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) offering FlowerStorm as well. Weeks after cybersecurity experts disrupted Rockstar2FA’s operations, Sophos noticed an uptick in the use of similar PhaaS portals believed to be part of FlowerStorm. The researchers identified 190 FlowerStorm indicators of compromise (IoCs) comprising 183 domains and seven IP addresses.
The WhoisXML API research team scoured the DNS for more artifacts possibly connected to the FlowerStorm infrastructure and uncovered:
A sample of the additional artifacts obtained from our analysis is available for download from our website.
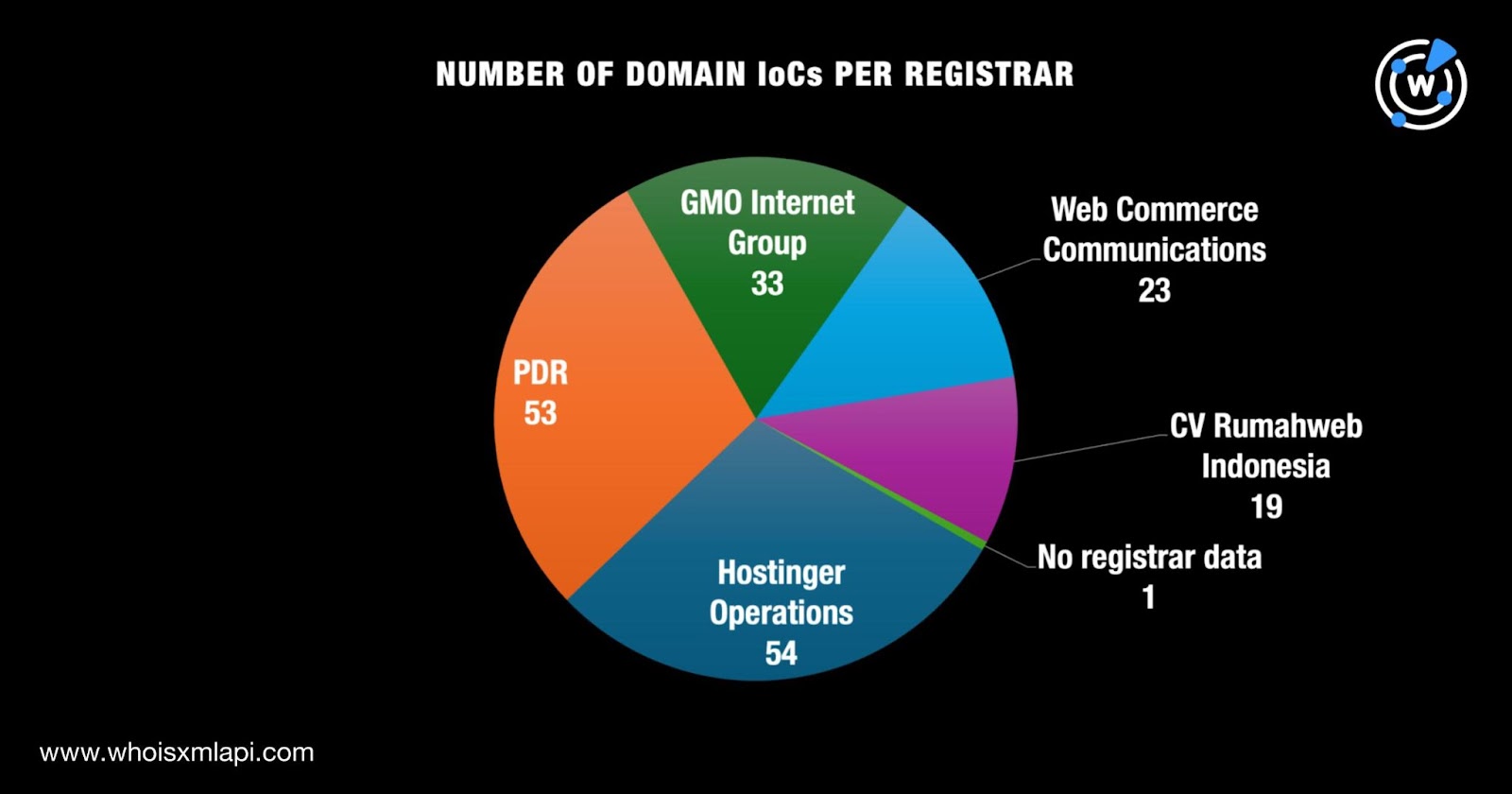
As is our usual first step to expand existing IoC lists, we looked more closely at the 183 domains tagged as IoCs.
A Bulk WHOIS API query for the 183 domains tagged as IoCs revealed that:
A majority of the domains, 107 to be exact, were registered in the U.S. A total of 23 IoCs were registered in Malaysia, while 19 were registered in Indonesia. Meanwhile, 34 domain IoCs did not have registrant country information in their current WHOIS records.

Next, we queried the 183 domains tagged as IoCs on DNS Chronicle API and found that 181 had 645 IP resolutions to date. Take a look at five other examples below.
| DOMAIN IoC | NUMBER OF IP RESOLUTIONS | FIRST IP RESOLUTION DATE |
|---|---|---|
| database-server[.]com | 45 | 6 October 2019 |
| 1069083060[.]site | 8 | 14 June 2024 |
| 5043056047[.]cloud | 7 | 9 July 2024 |
| 1616117488[.]site | 6 | 11 June 2024 |
| 1960373846[.]cloud | 5 | 2 July 2024 |
We then took a closer look at the seven IP addresses tagged as IoCs through a Bulk IP Geolocation Lookup query, which showed that:

A query on DNS Chronicle API for the seven IP addresses tagged as IoCs revealed that four had 2,019 domain resolutions over time. The IP address IoC 69[.]49[.]230[.]198 recorded the first domain resolution on 7 January 2022. Here are two other examples.
| IP ADDRESS IoC | NUMBER OF DOMAIN RESOLUTIONS | FIRST DOMAIN RESOLUTION DATE |
|---|---|---|
| 162[.]241[.]71[.]126 | 1,000 | 14 December 2022 |
| 43[.]153[.]176[.]84 | 19 | 7 September 2023 |
To kick off our search for connected artifacts, we queried the 183 domains tagged as IoCs on WHOIS History API and found that 34 had 15 email addresses in their historical WHOIS records after duplicates were filtered out. Upon closer examination, three of the addresses were public email addresses.
A Reverse WHOIS API query for the three public email addresses showed that two appeared in the current WHOIS records of 192 email-connected domains after duplicates and those already identified as IoCs were filtered out.
Next, we queried the 183 domains tagged as IoCs on DNS Lookup API, which revealed that 38 actively resolved to three IP addresses that have not yet been named as IoCs.
This post only contains a snapshot of the full research. Download the complete findings and a sample of the additional artifacts on our website or contact us to discuss your intelligence needs for threat detection and response or other cybersecurity use cases.
Disclaimer: We take a cautionary stance toward threat detection and aim to provide relevant information to help protect against potential dangers. Consequently, it is possible that some entities identified as “threats” or “malicious” may eventually be deemed harmless upon further investigation or changes in context. We strongly recommend conducting supplementary investigations to corroborate the information provided herein.
Sponsored byRadix

Sponsored byWhoisXML API

Sponsored byVerisign

Sponsored byVerisign

Sponsored byDNIB.com

Sponsored byCSC

Sponsored byIPv4.Global
