

 Negotiation processes in the UN are remembered not just for what came out of them, but also for what they were like, who participated, and how they were conducted. People who participated in the first World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) back in 2003 and 2005 often talk about the process, its challenges and its achievements.
Negotiation processes in the UN are remembered not just for what came out of them, but also for what they were like, who participated, and how they were conducted. People who participated in the first World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) back in 2003 and 2005 often talk about the process, its challenges and its achievements.
 Cyber criminals are the kings of recycling. Once they've found a tactic that works well, they'll keep doing it as long as they can get away with it. That's why it's so important for research teams to keep a close eye on what's happening behind the scenes with web traffic. Case in point? Our team at DNSFilter recently analyzed global DNS activity from the first quarter of 2025 and identified several notable trends.
Cyber criminals are the kings of recycling. Once they've found a tactic that works well, they'll keep doing it as long as they can get away with it. That's why it's so important for research teams to keep a close eye on what's happening behind the scenes with web traffic. Case in point? Our team at DNSFilter recently analyzed global DNS activity from the first quarter of 2025 and identified several notable trends.
 This past week offered a striking illustration of the pace and scale at which our shared orbital environment is evolving. In less than 24 hours, six rockets were launched from different parts of the globe, each contributing to the rapid expansion of low Earth orbit (LEO) infrastructure. China deployed a new set of Guowang satellites, while SpaceX launched two batches of Starlink satellites - one from Vandenberg in California and another from Cape Canaveral in Florida. United Launch Alliance (ULA) successfully placed Amazon's Kuiper satellites into orbit...
This past week offered a striking illustration of the pace and scale at which our shared orbital environment is evolving. In less than 24 hours, six rockets were launched from different parts of the globe, each contributing to the rapid expansion of low Earth orbit (LEO) infrastructure. China deployed a new set of Guowang satellites, while SpaceX launched two batches of Starlink satellites - one from Vandenberg in California and another from Cape Canaveral in Florida. United Launch Alliance (ULA) successfully placed Amazon's Kuiper satellites into orbit...
 Netscout recently released its latest Threat Intelligence Report that documents DDoS attacks in the second half of 2024. As has been the trend for many years, the largest target of DDoS attacks has been ISP networks. There were over 8.9 million DDoS attacks documented in the second half of last year, up 12.75% over the first half of the year.
Netscout recently released its latest Threat Intelligence Report that documents DDoS attacks in the second half of 2024. As has been the trend for many years, the largest target of DDoS attacks has been ISP networks. There were over 8.9 million DDoS attacks documented in the second half of last year, up 12.75% over the first half of the year.
 After several delays due to bad weather, Amazon's Project Kuiper finally launched its first batch of low-orbit broadband satellites on April 28. The company says it is in communication with all 27 new satellites. Amazon used a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket launched from Cape Canaveral. Amazon is under pressure to get the launches going and has a commitment to the FCC to launch 1,618 satellites by July 2026.
After several delays due to bad weather, Amazon's Project Kuiper finally launched its first batch of low-orbit broadband satellites on April 28. The company says it is in communication with all 27 new satellites. Amazon used a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V rocket launched from Cape Canaveral. Amazon is under pressure to get the launches going and has a commitment to the FCC to launch 1,618 satellites by July 2026.
 The story of computing and communications over the past eighty years has been a story of quite astounding improvements in the capability, cost and efficiency of computers and communications. If the same efficiency improvements had been made in the automobile industry cars would cost a couple of dollars, would cost fractions of a cent to use for trips, and be capable of travelling at speeds probably approaching the speed of light!
The story of computing and communications over the past eighty years has been a story of quite astounding improvements in the capability, cost and efficiency of computers and communications. If the same efficiency improvements had been made in the automobile industry cars would cost a couple of dollars, would cost fractions of a cent to use for trips, and be capable of travelling at speeds probably approaching the speed of light!
 The debate surrounding digital sovereignty has gained momentum in recent years, particularly within BRICS nations, where governments seek to assert greater control over their digital ecosystems. Proponents of digital sovereignty often frame it as a necessary countermeasure against foreign technological dominance, positioning it as either a "positive" force- fostering local innovation and self-reliance- or a "negative" one- fueling authoritarian control and economic isolation.
The debate surrounding digital sovereignty has gained momentum in recent years, particularly within BRICS nations, where governments seek to assert greater control over their digital ecosystems. Proponents of digital sovereignty often frame it as a necessary countermeasure against foreign technological dominance, positioning it as either a "positive" force- fostering local innovation and self-reliance- or a "negative" one- fueling authoritarian control and economic isolation.
 The World Summit on Information Society (WSIS) convened by World leaders in 2003 and 2005 following the realization of the crucial roles of Information and Communications Technologies (ICTs) (also known in the industry as the Internet) played in economic growth and development. Since 2005, ICTs have added more than $10tr to the global economy (Oxford Economics, 2020).
The World Summit on Information Society (WSIS) convened by World leaders in 2003 and 2005 following the realization of the crucial roles of Information and Communications Technologies (ICTs) (also known in the industry as the Internet) played in economic growth and development. Since 2005, ICTs have added more than $10tr to the global economy (Oxford Economics, 2020).
 Tech developments saw less drama than trade and environmental shifts during Trump's first 100 days. Continuity, not abrupt change, defined his approach to AI and digital regulation. Only 9 of 139 executive orders (EOs) focused on tech. Trump's tech policy emphasised reviews and incremental shifts. Public consultations on AI, cybersecurity, and cryptocurrencies signal steady evolution over upheaval.
Tech developments saw less drama than trade and environmental shifts during Trump's first 100 days. Continuity, not abrupt change, defined his approach to AI and digital regulation. Only 9 of 139 executive orders (EOs) focused on tech. Trump's tech policy emphasised reviews and incremental shifts. Public consultations on AI, cybersecurity, and cryptocurrencies signal steady evolution over upheaval.
 Dave Taht died on April 1st. I met him only recently, and never in person, but his passing saddens me. His technical work and evangelism have improved the Internet, and I will give some examples of his contributions to the Internet community and users, but I am sad because he was a good person -- idealistic, unselfish, open, and funny. I'll miss him. First, his contributions, then his values.
Dave Taht died on April 1st. I met him only recently, and never in person, but his passing saddens me. His technical work and evangelism have improved the Internet, and I will give some examples of his contributions to the Internet community and users, but I am sad because he was a good person -- idealistic, unselfish, open, and funny. I'll miss him. First, his contributions, then his values.
 When the Internet outgrew its academic and research roots and gained some prominence and momentum in the broader telecommunications environment, its proponents found themselves in opposition to many of the established practices of international telecommunications arrangements and even in opposition to the principles that lie behind these arrangements.
When the Internet outgrew its academic and research roots and gained some prominence and momentum in the broader telecommunications environment, its proponents found themselves in opposition to many of the established practices of international telecommunications arrangements and even in opposition to the principles that lie behind these arrangements.
 Last week, GPD, together with 114 organisations and 57 individual experts from civil society, the technical community, industry and academia, presented a set of cross-stakeholder community recommendations aimed at operationalising the modalities for the twenty-year review of the WSIS (WSIS+20). The open letter responds to the adoption on 25 March of a UN General Assembly resolution on WSIS+20 modalities, advocating for a transparent and inclusive review process that meaningfully engages all relevant stakeholders.
Last week, GPD, together with 114 organisations and 57 individual experts from civil society, the technical community, industry and academia, presented a set of cross-stakeholder community recommendations aimed at operationalising the modalities for the twenty-year review of the WSIS (WSIS+20). The open letter responds to the adoption on 25 March of a UN General Assembly resolution on WSIS+20 modalities, advocating for a transparent and inclusive review process that meaningfully engages all relevant stakeholders.
 When major events like the Super Bowl are on the horizon, cybercriminals exploit public trust by creating fraudulent domains for fake betting sites, phishing, and malware distribution. CSC's research into top online sportsbooks highlights the hidden risks of dormant domains, which, though inactive, can quickly be repurposed for cyber attacks. Overlooked yet dangerous, these domains play a key role in impersonation, misinformation, and scams targeting event-driven traffic, underscoring the need for continuous monitoring of lookalike, dropped, re-registered, and newly registered domains.
When major events like the Super Bowl are on the horizon, cybercriminals exploit public trust by creating fraudulent domains for fake betting sites, phishing, and malware distribution. CSC's research into top online sportsbooks highlights the hidden risks of dormant domains, which, though inactive, can quickly be repurposed for cyber attacks. Overlooked yet dangerous, these domains play a key role in impersonation, misinformation, and scams targeting event-driven traffic, underscoring the need for continuous monitoring of lookalike, dropped, re-registered, and newly registered domains.
 In January 2025, President Donald Trump -- now serving his second non-consecutive term -- unveiled a sweeping tariff regime designed to recalibrate America's global trade relationships. Among the measures was a blanket 10% tariff on all imported goods, accompanied by higher, so-called "reciprocal" tariffs targeting specific regions: 20% on EU imports and a dramatic 145% on goods from China. While these heightened rates were temporarily paused on April 9, 2025, for 90 days (excluding China), the 10% baseline tariff remains broadly in effect, symbolizing a shift toward an overtly protectionist economic doctrine.
In January 2025, President Donald Trump -- now serving his second non-consecutive term -- unveiled a sweeping tariff regime designed to recalibrate America's global trade relationships. Among the measures was a blanket 10% tariff on all imported goods, accompanied by higher, so-called "reciprocal" tariffs targeting specific regions: 20% on EU imports and a dramatic 145% on goods from China. While these heightened rates were temporarily paused on April 9, 2025, for 90 days (excluding China), the 10% baseline tariff remains broadly in effect, symbolizing a shift toward an overtly protectionist economic doctrine.
 You may have read our previous blog about the pending reduction of digital certificate life cycles to just 90 days. This past weekend, the issue gained momentum at the Certification Authority Browser Forum when more detail was discussed following the proposed ballot to set a timeline for shorter lifetime certificates by Apple. This creates real urgency for organizations of all sizes to seriously consider and implement automation into their certificate life cycle management.
You may have read our previous blog about the pending reduction of digital certificate life cycles to just 90 days. This past weekend, the issue gained momentum at the Certification Authority Browser Forum when more detail was discussed following the proposed ballot to set a timeline for shorter lifetime certificates by Apple. This creates real urgency for organizations of all sizes to seriously consider and implement automation into their certificate life cycle management.
 Massive Iberian Power Outage Raises Cybersecurity Questions
Massive Iberian Power Outage Raises Cybersecurity Questions Africa’s Digital Darkness: Internet Shutdowns Reach Record High
Africa’s Digital Darkness: Internet Shutdowns Reach Record High Massive Cyber Assault on X: Musk Hints at Foreign Involvement
Massive Cyber Assault on X: Musk Hints at Foreign Involvement Lack of Broadband Competition Leads to Higher Prices in Most U.S. Counties
Lack of Broadband Competition Leads to Higher Prices in Most U.S. Counties Meta’s Undersea Ambitions: A Cable to Power the AI Future
Meta’s Undersea Ambitions: A Cable to Power the AI Future India Launches ‘.bank.in’ and ‘.fin.in’ Domains to Deter Financial Fraud
India Launches ‘.bank.in’ and ‘.fin.in’ Domains to Deter Financial Fraud Baltic Sea Infrastructure Targeted Amid Rising Geopolitical Tensions
Baltic Sea Infrastructure Targeted Amid Rising Geopolitical Tensions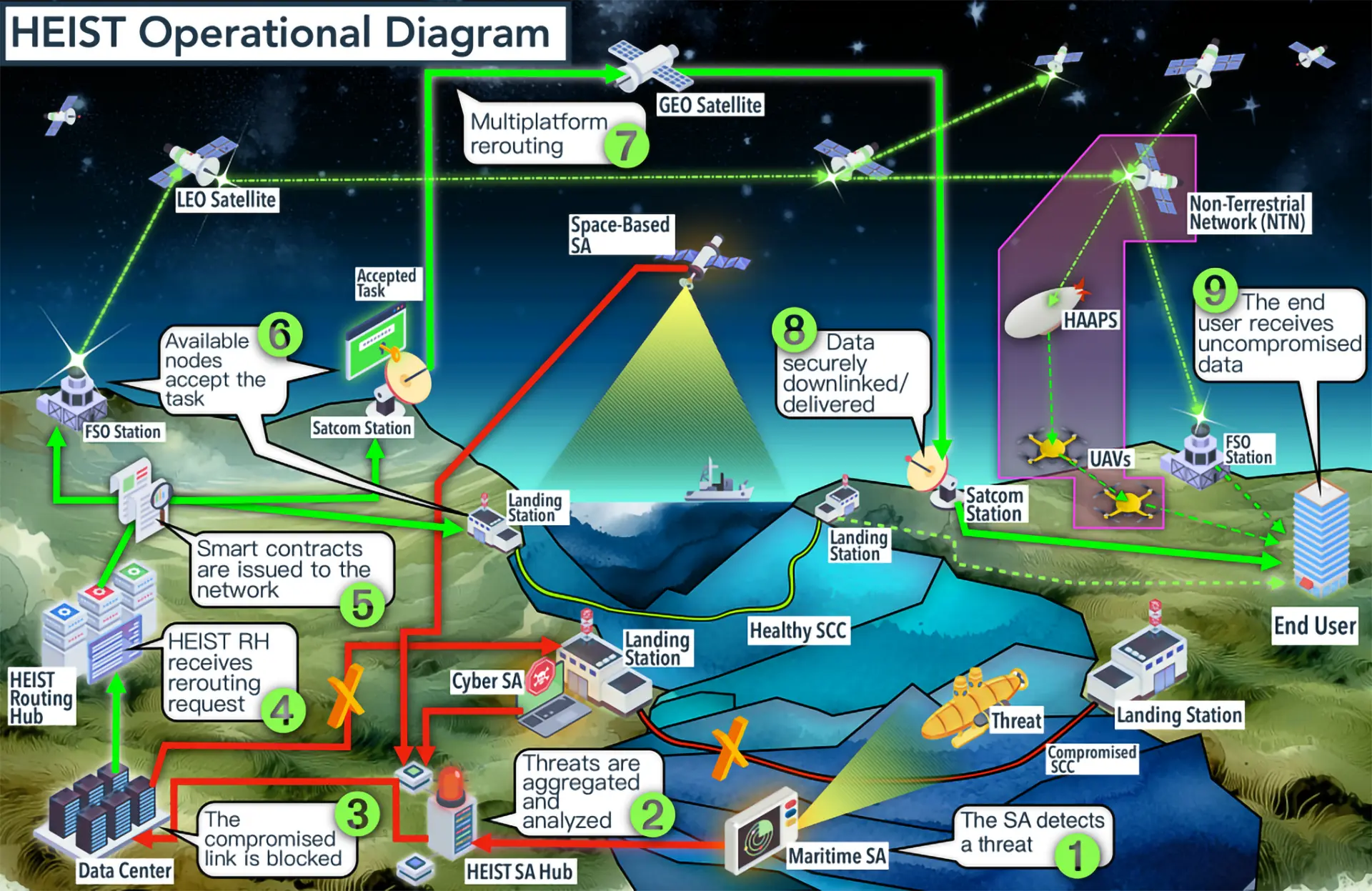 NATO’s Orbital Lifeline: A Backup Plan for the Internet
NATO’s Orbital Lifeline: A Backup Plan for the Internet Europe Seeks Space Independence with €10.6bn Iris² Satellite Network
Europe Seeks Space Independence with €10.6bn Iris² Satellite Network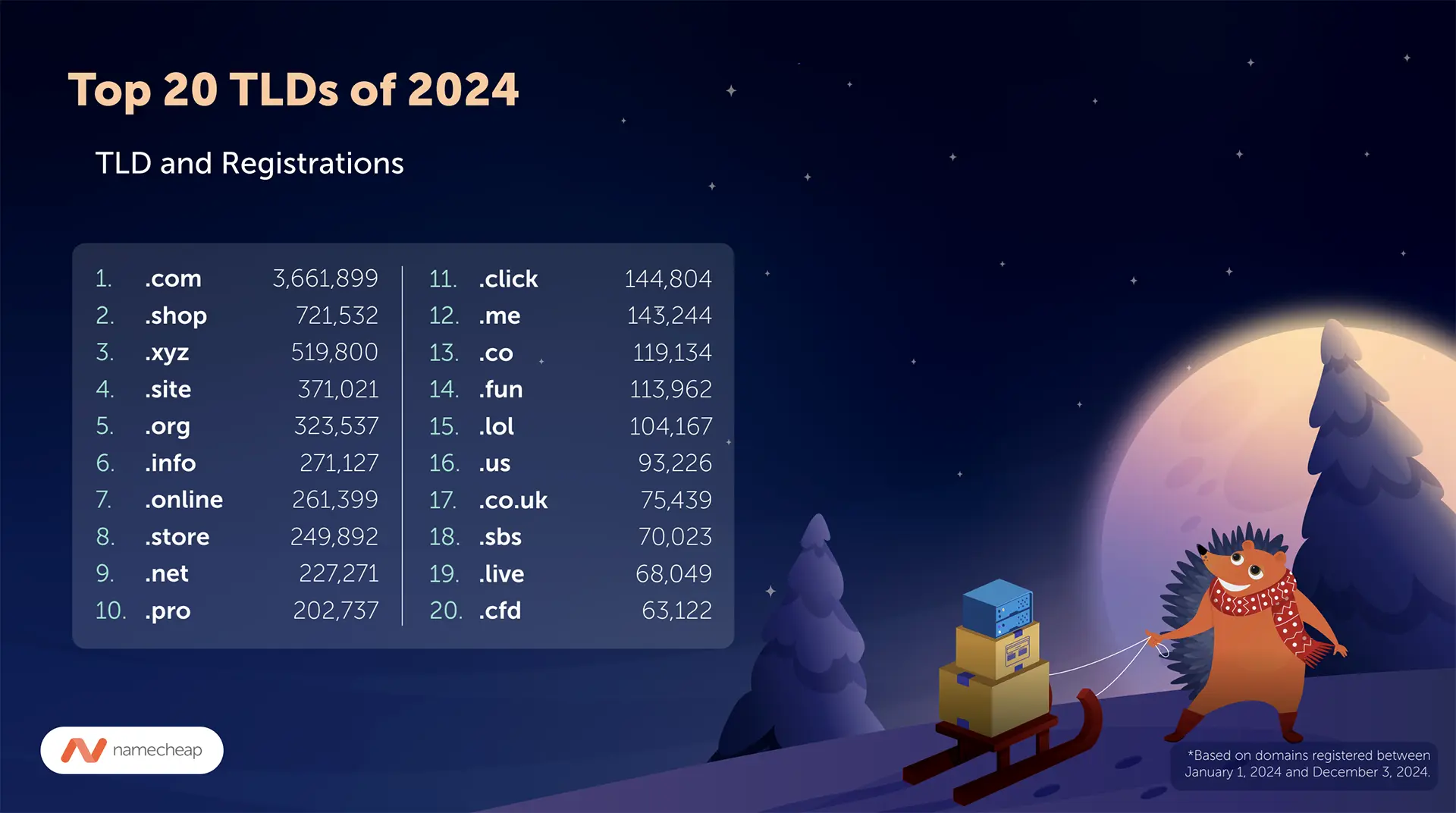 Domain Trends Signal Shifting Tides in 2024
Domain Trends Signal Shifting Tides in 2024 Chinese Hackers Exploit U.S. Telecom Systems, Eviction Efforts Lag
Chinese Hackers Exploit U.S. Telecom Systems, Eviction Efforts Lag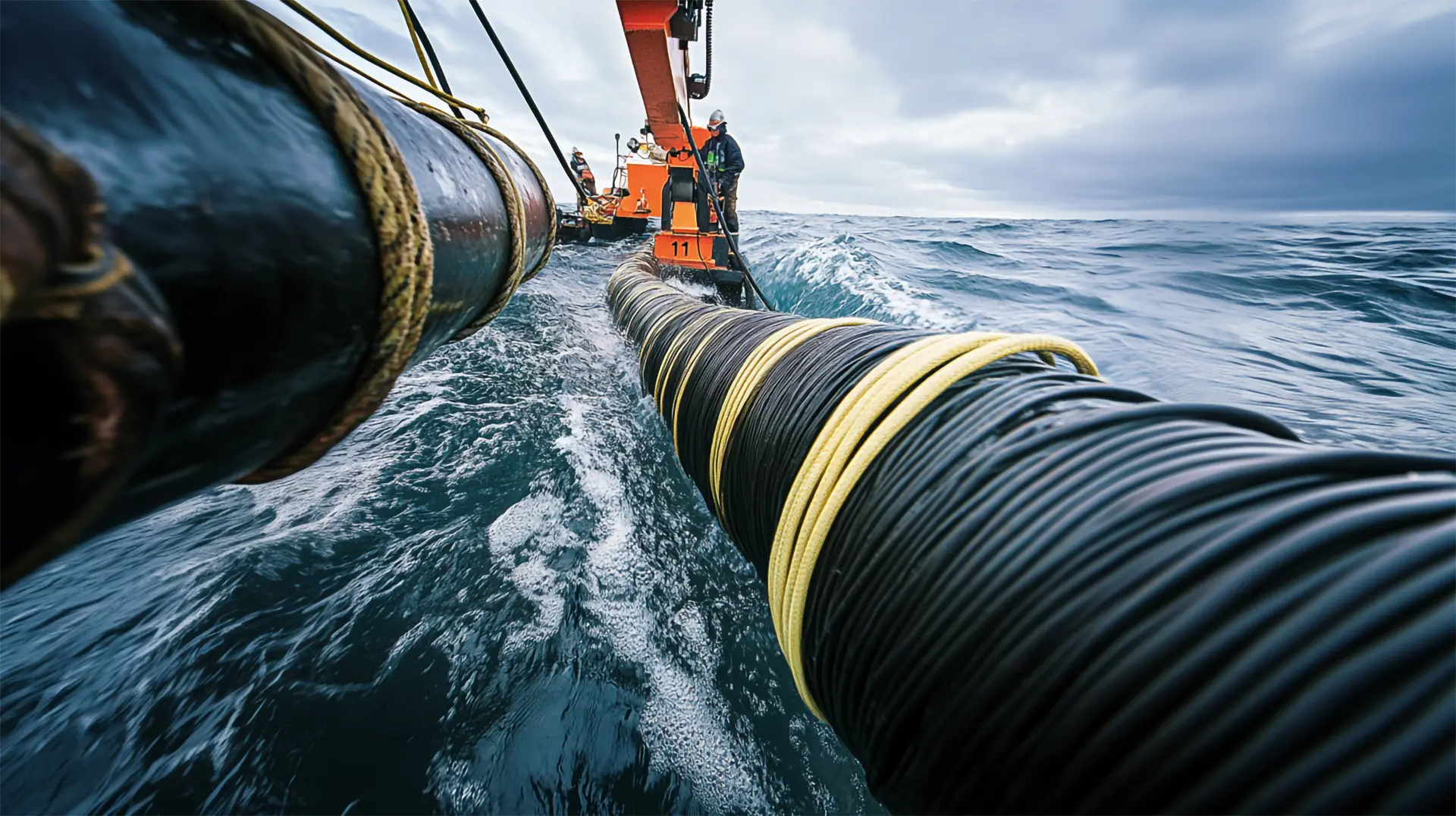 Meta’s $10 Billion Plan to Build the World’s Largest Subsea Cable Network
Meta’s $10 Billion Plan to Build the World’s Largest Subsea Cable Network